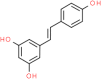
Resveratrol delays the progression of diabetic nephropathy through multiple pathways: A dose-response meta-analysis based on animal models
- PMID: 39264004
- PMCID: PMC11391385
- DOI: 10.1111/1753-0407.13608
Resveratrol delays the progression of diabetic nephropathy through multiple pathways: A dose-response meta-analysis based on animal models
Abstract
Objective: Accumulating experimental evidence has shown that resveratrol supplementation is effective for treating diabetic nephropathy (DN) in animal models. In this systematic review and meta-analysis, we assessed the effects and multiple mechanisms of resveratrol in animal models of DN.
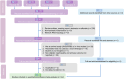
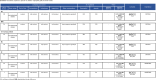
Methods: Before September 2023, preclinical literature was systematically searched and screened across PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library. Forty-two studies were included, and the risk of bias tool from SYRCLE was used to assess the methodological quality. Pooled overall effect sizes of the results were generated by STATA 16.0.
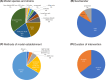
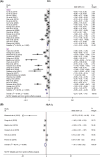
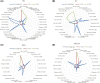
Results: The overall results provide preliminary evidence that the consumption of resveratrol can significantly reduce the mesangial index, glomerular basement membrane thickness, glomerular hypertrophy, serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, 24-h urinary protein, blood glucose, kidney index, total cholesterol, triglyceride, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. In contrast, the levels of albumin and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol are significantly increased. However, resveratrol did not significantly reduce creatinine clearance or glycated hemoglobin levels. Dose-response analysis revealed that resveratrol was most effective at improving kidney function and reducing DN when administered at lower doses of ≤15 mg/kg/day or higher doses of 100-200 mg/kg/day, with significant improvements in biochemical kidney injury markers and a better effect on dysglycemia.
Conclusions: The benefits of resveratrol in DN are likely due to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, metabolic regulatory, and autophagy-promoting effects. To confirm these findings for clinical use, further large-scale, long-term, high-quality preclinical trials are warranted to accurately assess the anti-DN effects and safety of resveratrol.
Keywords: animal model; diabetic nephropathy; meta‐analysis; renal pathology; resveratrol; systematic review.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Diabetes published by Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Selby NM, Taal MW. An updated overview of diabetic nephropathy: diagnosis, prognosis, treatment goals and latest guidelines. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020;22(Suppl 1):3‐15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

