Efficacy of Brodalumab in Patients with Psoriasis and Risk Factors for Treatment Failure: A Review of Post Hoc Analyses
- PMID: 39264399
- PMCID: PMC11480272
- DOI: 10.1007/s13555-024-01264-3
Efficacy of Brodalumab in Patients with Psoriasis and Risk Factors for Treatment Failure: A Review of Post Hoc Analyses
Abstract
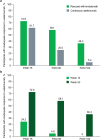
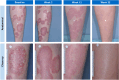
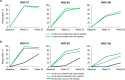
Factors such as obesity, alcohol consumption, and tobacco use are associated with both increased psoriasis severity and inadequate response to systemic and biologic therapies. Obesity is linked to chronic inflammation, which can contribute to psoriasis pathogenesis. Fixed-dose therapies may have reduced efficacy in patients with a higher body mass index, while weight-based dosing can increase the burden of drug-specific side effects. Alcohol and nicotine from tobacco have also been shown to stimulate keratinocyte and immune cell proliferation and production of proinflammatory cytokines. While these risk factors are prevalent among patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis, their influence on treatment outcomes may be overlooked when evaluating therapeutic options. Brodalumab is a fully human interleukin-17 receptor A antagonist approved for the treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis. In this review, we describe the lifestyle-related risk factors associated with decreased response to treatment. We further summarize the post hoc analyses of brodalumab in participant subgroups with moderate-to-severe psoriasis and a history of prior biologic failure, obesity, and alcohol or tobacco use from two phase 3 clinical trials (AMAGINE-2 and AMAGINE-3; ClinicalTrials.gov identifiers: NCT01708603 and NCT01708629, respectively). Our review of clinical trial and real-world data suggests that brodalumab is an efficacious and safe treatment option for patients with lifestyle factors that increase the likelihood of treatment failure, allowing them to achieve skin clearance and improve quality of life.
Keywords: Alcohol; Biologic therapy; IL-17 receptor A inhibitor; Obesity; Plaque psoriasis; Tobacco.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Mark G. Lebwohl is an employee of Mount Sinai; has received research funding from AbbVie, Amgen, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Avotres, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cara Therapeutics, Clexio Biosciences, Dermavant Sciences, Incyte, Inozyme, Janssen, Lilly, Ortho Dermatologics (a division of Bausch Health Companies Inc), Pfizer, Sanofi-Regeneron, and UCB; and has served as a consultant for Almirall, AltruBio, AnaptysBio, Apogee, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, AstraZeneca, Atomwise, Avotres Therapeutics, Brickell Biotech, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Castle Biosciences, Celltrion, CorEvitas, Dermavant Sciences, Dermsquared, EPI Health, Evommune, Facilitation of International Dermatology Education, Forte Biosciences, Foundation for Research and Education in Dermatology, Galderma, Genentech, Incyte, LEO Pharma, Meiji Seika Pharma, Mindera, Pfizer, Sanofi-Regeneron, Seanergy, Strata, Takeda, Trevi, and Verrica. April W. Armstrong has served as a research investigator, scientific advisor and/or speaker to AbbVie, Almirall, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, ASLAN, Beiersdorf, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Dermavant Sciences, Dermira, EPI Health, Incyte, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Lilly, Nimbus, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics (a division of Bausch Health Companies Inc), Pfizer, Sanofi-Regeneron, Sun Pharmaceuticals, and UCB. Andrew F. Alexis has received research funding from AbbVie, Amgen, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Castle Biosciences, Dermavant Sciences, Galderma, and LEO Pharma; has served as a consultant or advisory board member for AbbVie, Almirall, Allergan, Alphaeon, Alphyn, Amgen, Apogee, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Bausch Health Companies Inc, Beiersdorf, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Canfield Scientific, Cara Therapeutics, Castle Biosciences, Cutera, Dermavant Sciences, EPI Health, Galderma, Incyte, Janssen, Lilly, L’Oreal, Ortho Dermatologics (a division of Bausch Health Companies Inc), Pfizer, Sanofi-Regeneron, Swiss American, UCB, and VisualDx; has served as a speaker for Bristol-Myers Squibb, Johnson & Johnson, Janssen, L’Oreal, Regeneron, and Sanofi-Genzyme; and has received royalties from Springer, Wiley-Blackwell, and Wolters Kluwer Health and equipment from Aerolase. Edward L. Lain has served as an investigator, speaker, consultant, or advisory board member for AbbVie, Aclaris Therapeutics, AlfaSigma, Allergan, Almirall, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, AstraZeneca, Athenix, Biofrontera, Biopelle, BioPharmX, Biorasi, Brickell Biotech, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Cassiopea S.p.A, Castle Biosciences, Celgene, Cellceutix, ChemoCentryx, Concert Pharma, Cutanea, Dermavant Sciences, Dermira, Dermtech, Dow, Dr. Reddy's Laboratories, Endo Pharma, EPI Health, Evelo, Gage Development Company, Galderma Laboratories, Galderma, Hovione, Incyte, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson, Kadmon Corporation, La Roche-Posay, LEO Pharma, Lilly, MedImmune, Menlo Therapeutics, Mindera, Moleculin, Neothetics, Nielsen Holdings N.V, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics (a division of Bausch Health Companies Inc), Pierre Fabre, Pfizer, Promius Pharma, Sanofi, Sebacia, Sienna Labs, SkinCeuticals, Sol–Gel Technologies, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Symatese, Timber Pharma, UCB, Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America, and Vyne Therapeutics. Abby A. Jacobson is an employee of Bausch Health Companies Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Lebwohl M, Menter A, Lain E, Han G, Jacobson A. Long-term skin clearance with brodalumab in patients with psoriasis and inadequate response to prior biologics. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21(4):354–70. - PubMed
Publication types
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

