Emotional food craving across the eating disorder spectrum: an ecological momentary assessment study
- PMID: 39264507
- PMCID: PMC11393200
- DOI: 10.1007/s40519-024-01690-4
Emotional food craving across the eating disorder spectrum: an ecological momentary assessment study
Abstract
Purpose: Emotional eating during negative emotions might underlie disordered eating behavior (i.e., binge eating and food restriction). Positive emotions, by contrast, seem to promote healthier eating behavior. Naturalistic research on the links between emotions and eating across individuals with binge-eating disorder (BED), bulimia nervosa (BN), binge-purge anorexia nervosa (AN-BP), and restrictive anorexia nervosa (AN-R) is, however, lacking.
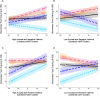
Methods: Individuals without eating disorders (comparison group, CG, n = 85), and patients with BED (n = 41), BN (n = 50), AN-BP (n = 26), and AN-R (n = 29) participated in an ecological momentary assessment study. Six daily notifications over eight days prompted ratings of momentary food craving and emotional states differing in valence and arousal.
Results: Results supported specific emotion-food-craving patterns in each group. Compared to the CG, arousing negative emotions and higher cravings co-occurred in patients with BN. In patients with AN-BP (at trend level also in patients with AN-R) less arousing negative emotions and lower cravings co-occurred. In patients with AN, positive emotions and higher cravings co-occurred whereas in patients with BED less arousing positive emotions and lower cravings co-occurred.
Conclusion: The found emotion-craving associations may underlie group-specific (dys-)functional eating behaviors, i.e., binge eating and food restriction during negative emotions in patients with BN and AN, and normalized appetitive responses during positive emotions in patients with BED and AN. Therapeutic efforts could target arousing negative emotions in patients with BN, and less arousing negative emotions in patients with AN. Positive emotions could be used in a salutogenetic approach in patients with BED and AN.
Keywords: Eating disorders; Ecological momentary assessment; Emotional eating; Emotions; Experience sampling method; Food craving.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lavender JM, Utzinger LM, Cao L, Wonderlich SA, Engel SG, Mitchell JE et al (2016) Reciprocal associations between negative affect, binge eating, and purging in the natural environment in women with bulimia nervosa. J Abnorm Psychol 125(3):381–6. 10.1037/abn0000135 10.1037/abn0000135 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Macht M, Simons G (2011) Emotional eating. In: Nyklícek I, Vingerhoets A, Zeelenberg M (eds) Emotion regulation and well-being. Springer, New York
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

