Aging-related biomarkers for the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease based on bioinformatics analysis and machine learning
- PMID: 39264583
- PMCID: PMC11424590
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205954
Aging-related biomarkers for the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease based on bioinformatics analysis and machine learning
Abstract
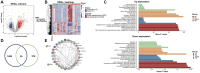
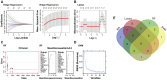
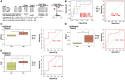
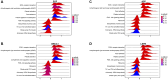
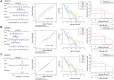
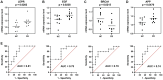
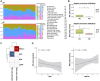
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a multifactorial disease that lacks reliable biomarkers for its diagnosis. It is now clear that aging is the greatest risk factor for developing PD. Therefore, it is necessary to identify novel biomarkers associated with aging in PD. In this study, we downloaded aging-related genes from the Human Ageing Gene Database. To screen and verify biomarkers for PD, we used whole-blood RNA-Seq data from 11 PD patients and 13 healthy control (HC) subjects as a training dataset and three datasets retrieved from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database as validation datasets. Using the limma package in R, 1435 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were found in the training dataset. Of these genes, 29 genes were found to occur in both DEGs and 307 aging-related genes. By using machine learning algorithms (LASSO, RF, SVM, and RR), Venn diagrams, and LASSO regression, four of these genes were determined to be potential PD biomarkers; these were further validated in external validation datasets and by qRT-PCR in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of 10 PD patients and 10 HC subjects. Based on the biomarkers, a diagnostic model was developed that had reliable predictive ability for PD. Two of the identified biomarkers demonstrated a meaningful correlation with immune cell infiltration status in the PD patients and HC subjects. In conclusion, four aging-related genes were identified as robust diagnostic biomarkers and may serve as potential targets for PD therapeutics.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; aging; diagnostic biomarker; machine learning algorithms; nomogram.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

