Investigating the Use of Traveltime and Reflection Tomography for Deep Learning-Based Sound-Speed Estimation in Ultrasound Computed Tomography
- PMID: 39264782
- PMCID: PMC11875925
- DOI: 10.1109/TUFFC.2024.3459391
Investigating the Use of Traveltime and Reflection Tomography for Deep Learning-Based Sound-Speed Estimation in Ultrasound Computed Tomography
Abstract
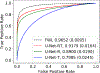
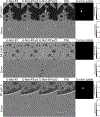
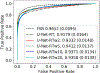
Ultrasound computed tomography (USCT) quantifies acoustic tissue properties such as the speed-of-sound (SOS). Although full-waveform inversion (FWI) is an effective method for accurate SOS reconstruction, it can be computationally challenging for large-scale problems. Deep learning-based image-to-image learned reconstruction (IILR) methods can offer computationally efficient alternatives. This study investigates the impact of the chosen input modalities on IILR methods for high-resolution SOS reconstruction in USCT. The selected modalities are traveltime tomography (TT) and reflection tomography (RT), which produce a low-resolution SOS map and a reflectivity map, respectively. These modalities have been chosen for their lower computational cost relative to FWI and their capacity to provide complementary information: TT offers a direct SOS measure, while RT reveals tissue boundary information. Systematic analyses were facilitated by employing a virtual USCT imaging system with anatomically realistic numerical breast phantoms (NBPs). Within this testbed, a supervised convolutional neural network (CNN) was trained to map dual-channel (TT and RT images) to a high-resolution SOS map. Single-input CNNs were trained separately using inputs from each modality alone (TT or RT) for comparison. The accuracy of the methods was systematically assessed using normalized root-mean-squared error (NRMSE), structural similarity index measure (SSIM), and peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR). For tumor detection performance, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was employed. The dual-channel IILR method was also tested on clinical human breast data. Ensemble average of the NRMSE, SSIM, and PSNR evaluated on this clinical dataset was 0.2355, 0.8845, and 28.33 dB, respectively.
Figures






References
-
- Duric N et al. , “Detection of breast cancer with ultrasound tomography: First results with the computed ultrasound risk evaluation (CURE) prototype,” Med. Phys, vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 773–785, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Duric N et al. , “Clinical breast imaging with ultrasound tomography: A description of the SoftVue system,” J. Acoust. Soc. Amer, vol. 135, no. 4, p. 2155, Apr. 2014.
-
- André M, Wiskin J, and Borup D, “Clinical results with ultrasound computed tomography of the breast,” in Quantitative Ultrasound in Soft Tissues. Cham, Switzerland: Springer, 2013, pp. 395–432.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

