Turning the needle into the haystack: Culture-independent amplification of complex microbial genomes directly from their native environment
- PMID: 39264872
- PMCID: PMC11392400
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012418
Turning the needle into the haystack: Culture-independent amplification of complex microbial genomes directly from their native environment
Abstract
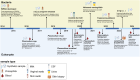
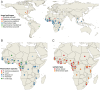
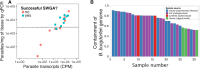
High-throughput sequencing (HTS) has revolutionized microbiology, but many microbes exist at low abundance in their natural environment and/or are difficult, if not impossible, to culture in the laboratory. This makes it challenging to use HTS to study the genomes of many important microbes and pathogens. In this review, we discuss the development and application of selective whole genome amplification (SWGA) to allow whole or partial genomes to be sequenced for low abundance microbes directly from complex biological samples. We highlight ways in which genomic data generated by SWGA have been used to elucidate the population dynamics of important human pathogens and monitor development of antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of potential outbreaks. We also describe the limitations of this method and propose some potential innovations that could be used to improve the quality of SWGA and lower the barriers to using this method across a wider range of infectious pathogens.
Copyright: © 2024 Pilling et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

