Peak amplitude of the normalized power spectrum of the electromyogram of the uterus in the low frequency band is an effective predictor of premature birth
- PMID: 39264880
- PMCID: PMC11392270
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308797
Peak amplitude of the normalized power spectrum of the electromyogram of the uterus in the low frequency band is an effective predictor of premature birth
Abstract
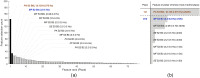
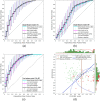
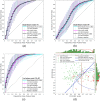
The current trends in the development of methods for non-invasive prediction of premature birth based on the electromyogram of the uterus, i.e., electrohysterogram (EHG), suggest an ever-increasing use of large number of features, complex models, and deep learning approaches. These "black-box" approaches rarely provide insights into the underlying physiological mechanisms and are not easily explainable, which may prevent their use in clinical practice. Alternatively, simple methods using meaningful features, preferably using a single feature (biomarker), are highly desirable for assessing the danger of premature birth. To identify suitable biomarker candidates, we performed feature selection using the stabilized sequential-forward feature-selection method employing learning and validation sets, and using multiple standard classifiers and multiple sets of the most widely used features derived from EHG signals. The most promising single feature to classify between premature EHG records and EHG records of all other term delivery modes evaluated on the test sets appears to be Peak Amplitude of the normalized power spectrum (PA) of the EHG signal in the low frequency band (0.125-0.575 Hz) which closely matches the known Fast Wave Low (FWL) frequency band. For classification of EHG records of the publicly available TPEHG DB, TPEHGT DS, and ICEHG DS databases, using the Partition-Synthesis evaluation technique, the proposed single feature, PA, achieved Classification Accuracy (CA) of 76.5% (AUC of 0.81). In combination with the second most promising feature, Median Frequency (MF) of the power spectrum in the frequency band above 1.0 Hz, which relates to the maternal resting heart rate, CA increased to 78.0% (AUC of 0.86). The developed method in this study for the prediction of premature birth outperforms single-feature and many multi-feature methods based on the EHG, and existing non-invasive chemical and molecular biomarkers. The developed method is fully automatic, simple, and the two proposed features are explainable.
Copyright: © 2024 Pirnar et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Born Too Soon—The Global Action Report on Preterm Birth. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2012. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241503433.
-
- Perin J, Mulick A, Yeung D, Villavicencio F, Lopez G, Strong KL, et al. Global, regional, and national causes of under-5 mortality in 2000-19: an updated systematic analysis with implications for the Sustainable Development Goals. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2022;6:106–115. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(21)00311-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kenny LC, Myers JE, editors. Obstetrics by ten teachers. 20th ed. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press; 2017. 10.1201/9781315382401 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

