Glaesserella parasuis serotype 4 exploits fibronectin via RlpA for tracheal colonization following porcine circovirus type 2 infection
- PMID: 39264911
- PMCID: PMC11392263
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012513
Glaesserella parasuis serotype 4 exploits fibronectin via RlpA for tracheal colonization following porcine circovirus type 2 infection
Abstract
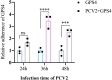
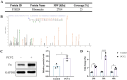
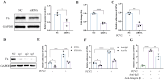
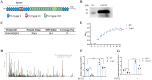
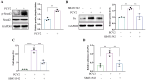
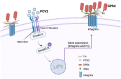
Porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) often causes disease through coinfection with other bacterial pathogens, including Glaesserella parasuis (G. parasuis), which causes high morbidity and mortality, but the role played by PCV2 and bacterial and host factors contributing to this process have not been defined. Bacterial attachment is assumed to occur via specific receptor-ligand interactions between adhesins on the bacterial cell and host proteins adsorbed to the implant surface. Mass spectrometry (MS) analysis of PCV2-infected swine tracheal epithelial cells (STEC) revealed that the expression of Extracellular matrix protein (ECM) Fibronectin (Fn) increased significantly on the infected cells surface. Importantly, efficient G. parasuis serotype 4 (GPS4) adherence to STECs was imparted by interactions with Fn. Furthermore, abrogation of adherence was gained by genetic knockout of Fn, Fn and Integrin β1 antibody blocking. Fn is frequently exploited as a receptor for bacterial pathogens. To explore the GPS4 adhesin that interacts with Fn, recombinant Fn N-terminal type I and type II domains were incubated with GPS4, and the interacting proteins were pulled down for MS analysis. Here, we show that rare lipoprotein A (RlpA) directly interacts with host Fibronectin mediating GPS4 adhesion. Finally, we found that PCV2-induced Fibronectin expression and adherence of GPS4 were prevented significantly by TGF-β signaling pathway inhibitor SB431542. Our data suggest the RlpA-Fn interaction to be a potentially promising novel therapeutic target to combat PCV2 and GPS4 coinfection.
Copyright: © 2024 Guo et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Liu M, Wang Q, Wu W, Chen M, Zhang P, Guo M, et al.. Glaesserella parasuis serotype 5 breaches the porcine respiratory epithelial barrier by inducing autophagy and blocking the cell membrane Claudin-1 replenishment. PLoS Pathog. 2022;18(10):e1010912. Epub 2022/10/14. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010912 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

