Extrapolating Lessons from Targeted Protein Degradation to Other Proximity-Inducing Drugs
- PMID: 39264973
- PMCID: PMC11494510
- DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.4c00191
Extrapolating Lessons from Targeted Protein Degradation to Other Proximity-Inducing Drugs
Abstract
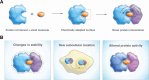
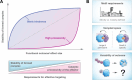
Targeted protein degradation (TPD) is an emerging pharmacologic strategy. It relies on small-molecule "degraders" that induce proximity of a component of an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex and a target protein to induce target ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation. Essentially, degraders thus expand the function of E3 ligases, allowing them to degrade proteins they would not recognize in the absence of the small molecule. Over the past decade, insights gained from identifying, designing, and characterizing various degraders have significantly enhanced our understanding of TPD mechanisms, precipitating in rational degrader discovery strategies. In this Account, I aim to explore how these insights can be extrapolated to anticipate both opportunities and challenges of utilizing the overarching concept of proximity-inducing pharmacology to manipulate other cellular circuits for the dissection of biological mechanisms and for therapeutic purposes.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares the following competing financial interest(s): G.E.W. is a scientific founder and shareholder of Proxygen and Solgate and on the Scientific Advisory Board of Nexo Therapeutics. The Winter lab received research funding from Pfizer.
Figures



References
-
- Oprea T. I.; Bologa C. G.; Brunak S.; Campbell A.; Gan G. N.; Gaulton A.; Gomez S. M.; Guha R.; Hersey A.; Holmes J.; Jadhav A.; Jensen L. J.; Johnson G. L.; Karlson A.; Leach A. R.; Ma’ayan A.; Malovannaya A.; Mani S.; Mathias S. L.; McManus M. T.; Meehan T. F.; von Mering C.; Muthas D.; Nguyen D.-T.; Overington J. P.; Papadatos G.; Qin J.; Reich C.; Roth B. L.; Schürer S. C.; Simeonov A.; Sklar L. A.; Southall N.; Tomita S.; Tudose I.; Ursu O.; Vidović D.; Waller A.; Westergaard D.; Yang J. J.; Zahoránszky-Köhalmi G. Unexplored Therapeutic Opportunities in the Human Genome. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 2018, 17 (5), 317–332. 10.1038/nrd.2018.14. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

