Effects of hesperidin, thymol, rosmarinic acid and their combined effect on growth performance, intestinal barrier function and cecal microbiota in broilers
- PMID: 39265517
- PMCID: PMC11416348
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104247
Effects of hesperidin, thymol, rosmarinic acid and their combined effect on growth performance, intestinal barrier function and cecal microbiota in broilers
Abstract
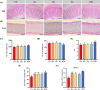
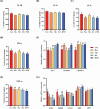
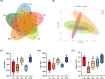
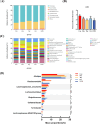
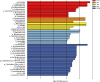
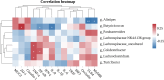
This study aims to investigate the effects of hesperidin (Hes), thymol (Thy), rosmarinic acid (RA) and their combined effect on broiler growth performance, intestinal barrier function, and cecal microbiota. A total of 240 newly hatched Arbor Acres broiler chicks were randomly divided into 5 treatments with 6 replicates of 8 chickens. The birds were fed a basal diet (Con group), a basal diet supplemented with 40 mg/kg Hes (Hes group), a basal diet supplemented with 40 mg/kg Thy (Thy group), a basal diet supplemented with 20 mg/kg RA (RA group), or a basal diet supplemented with 40 mg/kg Hes + 40 mg/kg Thy + 20 mg/kg RA (HTR group) for 42 d. The results indicated that dietary Hes and HTR supplementation enhanced average daily gain, final body weight, and eviscerated yield of broilers compared with the Con group (P < 0.05). Notably, the HTR treatment showed a decrease in abdominal fat yield and ratio of feed to weight gain (P < 0.05). HTR treatment increased ileal villus height, villus height/crypt depth, and number of goblet cells, decreased the crypt depth (P < 0.05), up-regulated the mRNA expression of tight junction proteins (ZO-1, Claudin-1, Occludin) and MUC2 (P < 0.05). Hes, Thy, RA, HTR treatment decreased the concentrations of pro-inflammatory factors (IL-8, IFN-γ and TNF-α), and down-regulated the mRNA expression of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB (P < 0.05). Importantly, the supplementation of HTR increased the relative abundance of beneficial bacteria (Parabacteroides, Lachnosiraceae NK4A136 and Turicbacter) and significantly decreased the relative abundance of opportunistic pathogenic bacteria such as Colidextribacter (P < 0.05). Additionally, the concentrations of propionate and butyrate in the cecum were elevated in the HTR group (P < 0.05). These findings indicate that the diet supplemented with HTR improved the growth performance and intestinal barrier function in broilers by modulating the cecal microbiota and its metabolites.
Keywords: broiler; hesperidin; intestinal barrier; rosmarinic acid; thymol.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES All authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Alagawany M., Abd El-Hack M.E., Farag M.R., Gopi M., Karthik K., Malik Y.S., and K.D. Rosmarinic acid: modes of action, medicinal values and health benefits. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2017;18:167–176. - PubMed
-
- Aoac I. Official methods of analysis of AOAC international. 18th ed. AOAC Int.; Arlington, VA: 2010.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

