Inhibition of WNK Kinases in NK Cells Disrupts Cellular Osmoregulation and Control of Tumor Metastasis
- PMID: 39265537
- PMCID: PMC11521464
- DOI: 10.1159/000540744
Inhibition of WNK Kinases in NK Cells Disrupts Cellular Osmoregulation and Control of Tumor Metastasis
Abstract
Introduction: The serine/threonine with-no-lysine (WNK) kinase family function in blood pressure control, electrolyte homeostasis, and cellular osmoregulation. These kinases and their downstream effectors are considered promising therapeutic targets in hypertension and stroke. However, the role of WNK kinases in immune cells remains poorly understood.
Methods: Using the small-molecule WNK kinase inhibitors WNK463 and WNK-IN-11, we investigated how WNK kinase inhibition affects natural killer (NK) cell physiology.
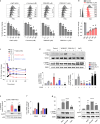
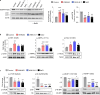
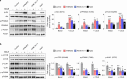
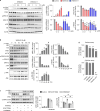
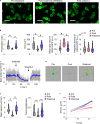
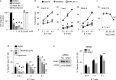
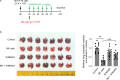
Results: WNK kinase inhibition with WNK463 or WNK-IN-11 significantly decreased IL-2-activated NK cell volume, motility, and cytolytic activity. Treatment of NK cells with these inhibitors induced autophagy by activating AMPK and inhibiting mTOR signaling. Moreover, WNK kinase inhibition increased phosphorylation of Akt and c-Myc by misaligning activity of activating kinases and inhibitory phosphatases. Treatment of tumor-bearing mice with WNK463 impaired tumor metastasis control by adoptively transferred NK cells.
Conclusion: The catalytic activity of WNK kinases has a critical role of multiple aspects of NK cell physiology and their pharmacologic inhibition negatively impacts NK cell function.
Keywords: Autophagy; Cytotoxicity; Natural killer; Osmoregulation; WNK kinases.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Figures
References
-
- Shekarabi M, Zhang J, Khanna AR, Ellison DH, Delpire E, Kahle KT. WNK kinase signaling in ion homeostasis and human disease. Cell Metab. 2017;25(2):285–99. - PubMed
-
- Verissimo F, Jordan P. WNK kinases, a novel protein kinase subfamily in multi-cellular organisms. Oncogene. 2001;20(39):5562–9. - PubMed
-
- Moriguchi T, Urushiyama S, Hisamoto N, Iemura S, Uchida S, Natsume T, et al. WNK1 regulates phosphorylation of cation-chloride-coupled cotransporters via the STE20-related kinases, SPAK and OSR1. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(52):42685–93. - PubMed
-
- Lalioti MD, Zhang J, Volkman HM, Kahle KT, Hoffmann KE, Toka HR, et al. Wnk4 controls blood pressure and potassium homeostasis via regulation of mass and activity of the distal convoluted tubule. Nat Genet. 2006;38(10):1124–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

