Somatic mutations in 3929 HPV positive cervical cells associated with infection outcome and HPV type
- PMID: 39266536
- PMCID: PMC11393421
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51713-y
Somatic mutations in 3929 HPV positive cervical cells associated with infection outcome and HPV type
Abstract
Invasive cervical cancers (ICC), caused by HPV infections, have a heterogeneous molecular landscape. We investigate the detection, timing, and HPV type specificity of somatic mutations in 3929 HPV-positive exfoliated cervical cell samples from individuals undergoing cervical screening in the U.S. using deep targeted sequencing in ICC cases, precancers, and HPV-positive controls. We discover a subset of hotspot mutations rare in controls (2.6%) but significantly more prevalent in precancers, particularly glandular precancer lesions (10.2%), and cancers (25.7%), supporting their involvement in ICC carcinogenesis. Hotspot mutations differ by HPV type, and HPV18/45-positive ICC are more likely to have multiple hotspot mutations compared to HPV16-positive ICC. The proportion of cells containing hotspot mutations is higher (i.e., higher variant allele fraction) in ICC and mutations are detectable up to 6 years prior to cancer diagnosis. Our findings demonstrate the feasibility of using exfoliated cervical cells for detection of somatic mutations as potential diagnostic biomarkers.
© 2024. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
M.P. is currently an employee of GlaxoSmithKline, J.F.B. and S.B. are now employees of AstraZeneca, and Amulya Shastry is now a doctoral student at Boston University, but they all completed the work associated with this project while employed at the National Cancer Institute. P.E.C. has received HPV tests and assays at a reduced or no cost for research from Roche, Becton Dickinson, Cepheid and Arbor Vita Corporation. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

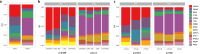


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- CA238592/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01 CA078527/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA238592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA078527/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001C/RC/CCR NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001E/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA78527/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- Intramural funds/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | NCI | Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics, National Cancer Institute (National Cancer Institute Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics)

