Adipocyte inflammation is the primary driver of hepatic insulin resistance in a human iPSC-based microphysiological system
- PMID: 39266553
- PMCID: PMC11393072
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-52258-w
Adipocyte inflammation is the primary driver of hepatic insulin resistance in a human iPSC-based microphysiological system
Abstract
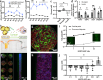
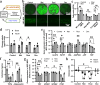
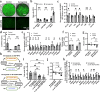
Interactions between adipose tissue, liver and immune system are at the center of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and type 2 diabetes. To address the need for an accurate in vitro model, we establish an interconnected microphysiological system (MPS) containing white adipocytes, hepatocytes and proinflammatory macrophages derived from isogenic human induced pluripotent stem cells. Using this MPS, we find that increasing the adipocyte-to-hepatocyte ratio moderately affects hepatocyte function, whereas macrophage-induced adipocyte inflammation causes lipid accumulation in hepatocytes and MPS-wide insulin resistance, corresponding to initiation of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. We also use our MPS to identify and characterize pharmacological intervention strategies for hepatic steatosis and systemic insulin resistance and find that the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist semaglutide improves hepatocyte function by acting specifically on adipocytes. These results establish our MPS modeling the adipose tissue-liver axis as an alternative to animal models for mechanistic studies or drug discovery in metabolic diseases.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GR 5417/1-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- R01 AR066735/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK026743/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- UG3 DK120004/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK026743/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

