Radiotherapy is recommended for hormone receptor-negative older breast cancer patients after breast conserving surgery
- PMID: 39266585
- PMCID: PMC11393351
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-66401-6
Radiotherapy is recommended for hormone receptor-negative older breast cancer patients after breast conserving surgery
Abstract
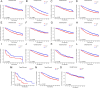
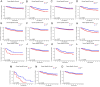
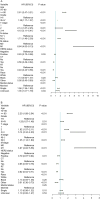
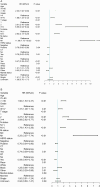
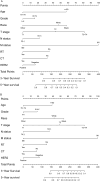
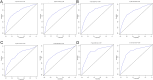
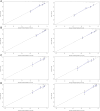
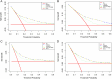
In this study, the necessity of radiotherapy (RT) for hormone receptor-negative older breast cancer patients after breast-conserving surgery (BCS) was investigated. The data of hormone receptor-negative invasive breast cancer patients who underwent BCS were extracted from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database from 2010 to 2015. All patients were separated into two groups, namely, the RT group and the no radiotherapy (No RT) group. The 3- and 5-year overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS) rates were compared between the No RT and RT groups after propensity score matching (PSM). The nomograms for predicting the survival of patients were constructed from variables identified by univariate or multivariate Cox regression analysis. A total of 2504 patients were enrolled in the training cohort, and 630 patients were included in the validation cohort. After PSM, 738 patients were enrolled in the No RT group and RT group. We noted that RT can improve survival in hormone receptor-negative older breast cancer patients who undergo BCS. Based on the results of multivariate Cox analysis, age, race, tumour grade, receipt of RT and chemotherapy, pathological T stage, N status, M status and HER2 status were linked to OS and CSS for these patients, and nomograms for predicting OS and CSS were constructed and validated. Moreover, RT improved OS and CSS in hormone receptor-negative older breast cancer patients who underwent BCS. In addition, the proposed nomograms more accurately predicted OS and CSS for hormone receptor-negative older breast cancer patients after BCS.
Keywords: Breast conserving surgery; Hormone receptor-negative older breast cancer patients; Nomograms; Prognosis; Radiotherapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Omitting Adjuvant Radiotherapy for Hormone Receptor‒Positive Early-Stage Breast Cancer in Old Age: A Propensity Score Matched SEER Analysis.Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Jan;51(1):326-336. doi: 10.4143/crt.2018.163. Epub 2018 May 10. Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 29747486 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of breast-conserving surgery without radiotherapy and mastectomy in the treatment of elderly patients with early breast cancer: A PSM and SEER database study.Cancer Med. 2023 Jul;12(14):15229-15245. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6210. Epub 2023 Jun 3. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 37269188 Free PMC article.
-
Can Radiotherapy After Breast-Conserving Surgery be Omitted in Elderly Patients with Early-Stage, Hormone-Receptor Negative Breast Cancer? A Population-Based Study and Proposed Nomogram.Adv Ther. 2022 Oct;39(10):4707-4722. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02279-y. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 35953665
-
Is neoadjuvant chemotherapy necessary for T2N0-1M0 hormone receptor-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer patients undergoing breast-conserving surgery?J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 May 30;150(5):285. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05810-6. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38814494 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and validation survival prediction models for T1 locally advanced breast cancer after breast conservation surgery versus mastectomy.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 9;15(1):12189. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91205-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40204827 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

