DMDD, isolated from Averrhoa carambola L., ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress-autophagy crosstalk
- PMID: 39267098
- PMCID: PMC11391757
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-024-00993-z
DMDD, isolated from Averrhoa carambola L., ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress-autophagy crosstalk
Abstract
Background: Studies have shown that Averrhoa carambola L. possesses therapeutic potential for diabetes and related complications. However, the specific beneficial effects and molecular mechanisms of 2-dodecyl-6-meth-oxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione (DMDD) isolated from Averrhoa carambola L. on diabetic nephropathy (DN) require further investigation.
Methods: 80 C57BL/6 J male mice were subjected to a 1-week adaptive feeding, followed by a high-fat diet and intraperitoneal injection of 100 mg/kg streptozotocin (STZ) to construct an in vivo DN model. Additionally, human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells (HK-2) induced by high glucose (HG) were used as an in vitro DN model. The expression levels of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS), and autophagy-related proteins in renal tubular cells were detected by Western Blot, flow cytometry, immunofluorescence, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) staining. Transcriptome analysis revealed was conducted to elucidate the specific mechanism of by which DMDD mitigates DN by inhibiting ERS and autophagy. HK-2 cells were transfected with IRE1α overexpression lentivirus to reveal the role of IRE1α overexpression in HG-induced HK-2.
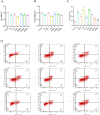
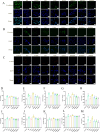
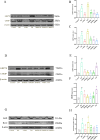
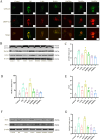
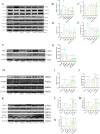
Results: The experimental data showed that DMDD significantly reduced blood glucose levels and improved renal pathological alterations in DN mice. Additionally, DMDD inhibited the calcium (Ca2+) pathway, manifested by decreased autophagosome formation and downregulation of LC3II/I, Beclin-1, and ATG5 expression. Moreover, in HG-induced HK-2 cells, DMDD suppressed the overexpression of GRP78, CHOP, LC3II/I, Beclin1, and ATG5. Notably, IRE1α overexpression significantly increased autophagy incidence; however, DMDD treatment subsequently reduced the expression of LC3II/I, Beclin1, and ATG5.
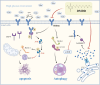
Conclusion: DMDD effectively inhibits excessive ERS and autophagy, thereby reducing renal cell apoptosis through the IRE1α pathway and Ca 2+ pathway.
Keywords: 2-Dodecyl-6-Meth-Oxycyclohexa-2,5-Diene-1,4-Dione; Autophagy; Diabetic nephropathy; Endoplasmic reticulum stress.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Yuan D, Liu XM, Fang Z, et al. Protective effect of resveratrol on kidney in rats with diabetic nephropathy and its effect on endoplasmic reticulum stress. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(5):1485–93. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

