Clinical benefit and safety profile of cross-line therapy with CDK4/6 inhibitors: a retrospective study of HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer
- PMID: 39267478
- PMCID: PMC11523273
- DOI: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2024.0204
Clinical benefit and safety profile of cross-line therapy with CDK4/6 inhibitors: a retrospective study of HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer
Abstract
Objective: CDK4/6 inhibitors (CDK4/6is) in combination with endocrine therapy have secured a central role in the treatment of hormone receptor (HR)-positive advanced breast cancer (ABC) and have transformed the therapeutic landscape. Cross-line CDK4/6i therapy in which another CDK4/6i is continued after progression on a prior CDK4/6i may still offer advantageous therapeutic effects. Cross-line CDK4/6i therapy is an area of active investigation in the ongoing pursuit to improve outcomes for patients with HR+/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)- ABC.
Methods: This retrospective study enrolled 82 patients with HR+/HER2- ABC who were treated with cross-line CDK4/6is (abemaciclib, palbociclib, ribociclib, and dalpiciclib) after progression with another CDK4/6i. The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS) according to version 1.1 of the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors. Secondary endpoints included toxicity, objective response rate, disease control rate, and overall survival. Adverse events (AEs) were graded according to version 5.0 of the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, as promulgated by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
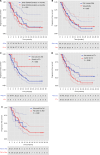
Results: Eighty-two HR+/HER2- ABC patients who received cross-line CDK4/6i therapy from January 2022 to February 2024 were enrolled. The median age of the patients was 60 years. The median PFS of all patients was 7.6 months (95% CI, 5.9-9.2). Cox regression analysis identified lung metastasis and a switch to endocrine therapy following prior CDK4/6i therapy as independent predictive factors for PFS. Notably, patients who previously received abemaciclib and switched to palbociclib upon disease progression had a median PFS of 10.7 months. The strategy of transitioning to chemotherapy after progression on a prior CDK4/6i, then to a subsequent CDK4/6i merits further investigation. Hematologic toxicity was the most common grade ≥ 3 AEs. No instances of fatal safety events were observed.
Conclusions: Cross-line CDK4/6i therapy is associated with significant clinical benefits and manageable safety profiles in patients with HR+/HER2- ABC, which underscores cross-line CDK4/6i therapy potential as an effective treatment strategy.
Keywords: Breast cancer; PFS; cross-line CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy; prior CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Real-world effectiveness comparison of first-line palbociclib, ribociclib or abemaciclib plus endocrine therapy in advanced HR-positive/HER2-negative BC patients: results from the multicenter PALMARES-2 study.Ann Oncol. 2025 Jul;36(7):762-774. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2025.03.023. Epub 2025 Apr 8. Ann Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40204155
-
Safety and quality of life of CDK4/6 inhibitors therapy for hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer: a multicenter cross-sectional survey in China.BMC Cancer. 2025 May 27;25(1):951. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14223-8. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40426093 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative overall survival of CDK4/6 inhibitors plus an aromatase inhibitor in HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer in the US real-world setting.ESMO Open. 2025 Jan;10(1):104103. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.104103. Epub 2025 Jan 3. ESMO Open. 2025. PMID: 39754979 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of ethnicity on cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor efficacy and toxicity: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Breast. 2025 Feb;79:103833. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2024.103833. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Breast. 2025. PMID: 39579620 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitors in hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 negative advanced breast cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Feb;180(1):21-32. doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-05528-2. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 31970560 Review.
References
-
- Giaquinto AN, Sung H, Miller KD, Kramer JL, Newman LA, Minihan A, et al. Breast Cancer Statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:524–541. - PubMed
-
- Huppert LA, Gumusay O, Idossa D, Rugo HS. Systemic therapy for hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative early stage and metastatic breast cancer. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73:480–515. - PubMed
-
- Morgan DO. Principles of CDK regulation. Nature. 1995;374:131–4. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
