Spatial Sensitivity to Absorption Changes for Various Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Methods: A Compendium Review
- PMID: 39267952
- PMCID: PMC11391891
- DOI: 10.1142/s1793545824300015
Spatial Sensitivity to Absorption Changes for Various Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Methods: A Compendium Review
Abstract
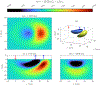
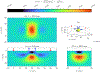
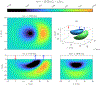
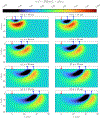
This compendium review focuses on the spatial distribution of sensitivity to localized absorption changes in optically diffuse media, particularly for measurements relevant to near-infrared spectroscopy. The three temporal domains, continuous-wave, frequency-domain, and time-domain, each obtain different optical data-types whose changes may be related to effective homogeneous changes in the absorption coefficient. Sensitivity is the relationship between a localized perturbation and the recovered effective homogeneous absorption change. Therefore, spatial sensitivity maps representing the perturbation location can be generated for the numerous optical data-types in the three temporal domains. The review first presents a history of the past 30 years of work investigating this sensitivity in optically diffuse media. These works are experimental and theoretical, presenting 1-, 2-, and 3-dimensional sensitivity maps for different near-infrared spectroscopy methods, domains, and data-types. Following this history, we present a compendium of sensitivity maps organized by temporal domain and then data-type. This compendium provides a valuable tool to compare the spatial sensitivity of various measurement methods and parameters in one document. Methods for one to generate these maps are provided in the appendix, including code. This historical review and comprehensive sensitivity map compendium provides a single source researchers may use to visualize, investigate, compare, and generate sensitivity to localized absorption change maps.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


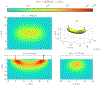
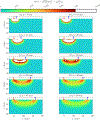
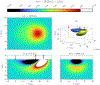

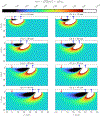


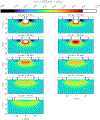
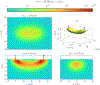
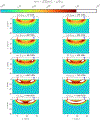

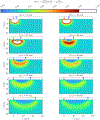

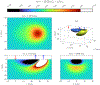

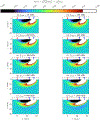
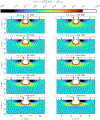
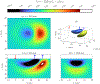
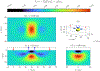
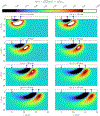

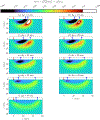
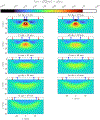
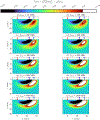
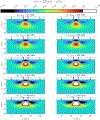
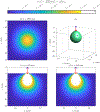

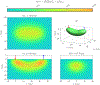
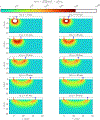



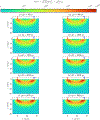
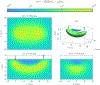





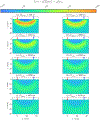








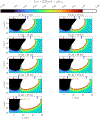
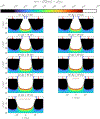
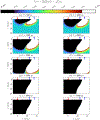
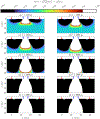



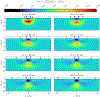
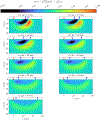

References
-
- Weiss George H., Nossal Ralph, and Bonner Robert F.. Statistics of Penetration Depth of Photons Reemitted from Irradiated Tissue. Journal of Modern Optics, 36(3):349–359, March 1989. ISSN 0950–0340. doi: 10.1080/09500348914550381. - DOI
-
- Barbour RL, Graber H, Aronson R, and Lubowsky J. Model For 3-D Optical Imaging Of Tissue. In 10th Annual International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, pages 1395–1399, May 1990. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.1990.688761. - DOI
-
- Schweiger Martin, Arridge Simon Robert, Hiraoka Mutsuhisa, and Delpy David T.. Application of the finite element method for the forward model in infrared absorption imaging. In Mathematical Methods in Medical Imaging, volume 1768, pages 97–108. SPIE, December 1992. doi: 10.1117/12.130893. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
