Research trends and hotspots on osteoporosis: a decade-long bibliometric and visualization analysis from 2014 to 2023
- PMID: 39267978
- PMCID: PMC11390546
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1436486
Research trends and hotspots on osteoporosis: a decade-long bibliometric and visualization analysis from 2014 to 2023
Abstract
Background: Osteoporosis is characterized by diminished bone density and quality, compromised bone microstructure, and increased bone fragility, culminating in a heightened risk of fracture. Relatively few attempts have been made to survey the breadth of osteoporosis research using bibliometric approaches. This study aims to delineate the current landscape of osteoporosis research, offering clarity and visualization, while also identifying potential future directions for investigation.
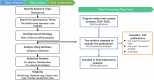
Methods: We retrieved and filtered articles and reviews pertaining to osteoporosis from the Web of Science Core Collection database, specifically the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-E) edition, spanning the years 2014 to 2023. Informatics tools such as CiteSpace and VOSviewer were employed to dissect the intellectual framework, discern trends, and pinpoint focal points of interest within osteoporosis research.
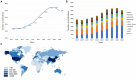
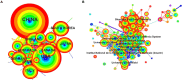
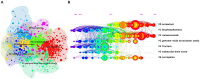
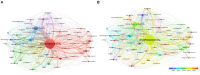
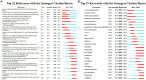
Results: Our dataset comprised 33,928 osteoporosis-related publications, with a notable surge in annual publication numbers throughout the last decade. China and the United States lead in terms of research output. The University of California System contributed substantially to this body of work, with Amgen demonstrating the highest degree of centrality within the network. Cooper Cyrus emerged as a pivotal figure in the field. An analysis of highly-cited studies, co-citation networks, and keyword co-occurrence revealed that recent years have predominantly concentrated on elucidating mechanisms underlying osteoporosis, as well as its diagnosis, prevention, and treatment strategies. Burst detection analyses of citations and keywords highlighted osteoblasts, sarcopenia, gut microbiota, and denosumab as contemporary hotspots within osteoporosis research.
Conclusion: This bibliometric analysis has provided a visual representation of the fundamental knowledge structure, prevailing trends, and key focal areas within osteoporosis research. The identification of osteoblasts, sarcopenia, gut microbiota, and denosumab as current hotspots may guide future research endeavors. Continued efforts directed at understanding the mechanisms, fracture outcomes, diagnostics, and therapeutics related to osteoporosis are anticipated to deepen our comprehension of this complex disease.
Keywords: CiteSpace; VOSviewer; bibliometric analysis; cited reference; osteoporosis.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Liu, Yu and Gu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

