Correlation of sputum inflammatory markers with severity and blood inflammatory markers in bronchiectasis
- PMID: 39268102
- PMCID: PMC11388234
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-24-573
Correlation of sputum inflammatory markers with severity and blood inflammatory markers in bronchiectasis
Abstract
Background: As a disease characterized by chronic neutrophilic inflammation, various sputum biomarkers have been investigated in the association with the severity and prognosis of bronchiectasis. However, there is lack of data on the association between sputum interleukin-1beta (IL-1β), interleukin-8 (IL-8) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) levels at clinical stable state and the clinical, spirometric and blood inflammatory parameters, as well as prognostic scores. The purpose of the study is to assess the association between sputum IL-1β, IL-8 and TNF-α levels at clinical stable state and various clinical and laboratory parameters in bronchiectasis.
Methods: A prospective study was conducted in a major regional hospital and tertiary respiratory referral centre in Hong Kong, including 44 Chinese patients with bronchiectasis. The correlation between stable state sputum IL-1β, IL-8 and TNF-α levels with various clinical, laboratory and spirometric parameters in bronchiectasis, as well as FACED [forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), age, chronic colonisation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, radiological extension and dyspnoea]/E-FACED (FACED plus exacerbations) scores were assessed.
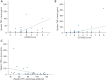
Results: Baseline sputum IL-1β level was found to have significant moderate positive correlation with baseline blood high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) level with Pearson correlation coefficient (r) of 0.529 (P=0.001). Baseline sputum IL-8 level was found to have significant moderate positive correlation with baseline FACED and E-FACED score with r of 0.574 (P<0.001) and 0.539 (P<0.001) respectively. Baseline sputum TNF-α level was found to have significant moderate positive correlation with baseline FACED score with r of 0.520 (P<0.001).
Conclusions: Sputum IL-1β and, IL-8 and TNF-α levels were shown to have significant correlation with various clinical, laboratory and spirometry parameters in bronchiectasis, as well as more severe disease as measured by FACED and E-FACED scores.
Keywords: Bronchiectasis; interleukin-1beta (IL-1β); interleukin-8 (IL-8); sputum cytokines; tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α).
2024 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-24-573/coif). W.C.K. reports that the study was supported by the Hong Kong College of Physicians Young Investigator Research Grant, Hong Kong College of Physicians. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
