The future of pharmacology and therapeutics of the arachidonic acid cascade in the next decade: Innovative advancements in drug repurposing
- PMID: 39268466
- PMCID: PMC11390530
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1472396
The future of pharmacology and therapeutics of the arachidonic acid cascade in the next decade: Innovative advancements in drug repurposing
Abstract
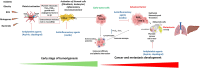
Many drugs can act on multiple targets or disease pathways, regardless of their original purpose. Drug repurposing involves reevaluating existing compounds for new medical uses. This can include repositioning approved drugs, redeveloping unapproved drugs, or repurposing any chemical, nutraceutical, or biotherapeutic product for new applications. Traditional drug development is slow, expensive, and has high failure rates. Drug repurposing can speed up the process, costing less and saving time. This approach can save 6-7 years of early-stage research time. Drug repurposing benefits from existing compounds with optimized structures and approved for clinical use with associated structure-activity relationship publications, supporting the development of new effective compounds. Drug repurposes can now utilize advanced in silico screening enabled by artificial intelligence (AI) and sophisticated tissue and organ-level in vitro models. These models more accurately replicate human physiology and improve the selection of existing drugs for further pre-clinical testing and, eventually, clinical trials for new indications. This mini-review discusses some examples of drug repurposing and novel strategies for further development of compounds for targets of the arachidonic acid cascade. In particular, we will delve into the prospect of repurposing antiplatelet agents for cancer prevention and addressing the emerging noncanonical functionalities of 5-lipoxygenase, potentially for leukemia therapy.
Keywords: 5-lipoxygenase; antiplatelet agents; cancer; drug repurposing; systems biology and network analysis.
Copyright © 2024 Patrignani, Contursi, Tacconelli and Steinhilber.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

