Ferulic acid suppresses the inflammation and apoptosis in Kawasaki disease through activating the AMPK/mTOR/NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 39268468
- PMCID: PMC11390509
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1420602
Ferulic acid suppresses the inflammation and apoptosis in Kawasaki disease through activating the AMPK/mTOR/NF-κB pathway
Abstract
Background: Kawasaki disease (KD) is a self-limiting and acute systemic vasculitis of unknown etiology, mainly affecting children. Ferulic acid (FA), a natural phenolic substance, has multiple pharmacological properties, including anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptosis, and anti-fibrosis, and so on. So far, the protective effects of FA on KD have not been explored.
Methods: In this study, we established Candida albicans water soluble fraction (CAWS)-induced mouse coronary artery vasculitis of KD model and the tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α)-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) injury model to investigate the anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptosis effects of FA on KD, and try to elucidate the underlying mechanism.
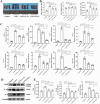
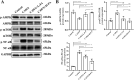
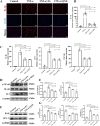
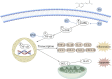
Results: Our in vivo results demonstrated that FA exerted anti-inflammatory effects on KD by inhibiting the infiltration of CD45-positive leukocytes and fibrosis around the coronary artery. Additionally, FA downregulated the levels of inflammatory and chemotactic cytokines, alleviated splenomegaly, and exhibited anti-apoptotic effects on KD by reducing TUNEL-positive cells, downregulating BAX expression, and upregulating BCL-2 expression. In addition, Our in vitro findings showed that FA could effectively inhibit TNF-α-induced HUVEC inflammation like NF-κB inhibitor QNZ by downregulating the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines as well as attenuated TNF-α-induced HUVEC apoptosis by reducing apoptotic cell numbers and the BAX/BCL-2 ratio, which could be reversed by the AMPK inhibitor compound c (CC). The further mechanistic study demonstrated that FA could restrain vascular endothelial cell inflammation and apoptosis in KD through activating the AMPK/mTOR/NF-κB pathway. However, FA alone is hard to completely restore KD into normal condition.
Conclusion: In conclusion, FA has potential protective effects on KD, suggesting its promising role as an adjuvant for KD therapy in the future.
Keywords: apoptosis; coronary artery; ferulic acid (FA); inflammation; kawasaki disease (KD); vasculitis.
Copyright © 2024 Wu, Wang, Tan, Ran, Guan, Qian, Feng, Jiang, Peng, Sheng, Xi, Ji and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Ahmad A., Biersack B., Li Y., Kong D., Bao B., Schobert R., et al. (2013). Targeted regulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR/NF-κB signaling by indole compounds and their derivatives: mechanistic details and biological implications for cancer therapy. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 13 (7), 1002–1013. 10.2174/18715206113139990078 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

