Free circulating versus extracellular vesicle-associated microRNA expression in canine T-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 39268522
- PMCID: PMC11390581
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1461506
Free circulating versus extracellular vesicle-associated microRNA expression in canine T-cell lymphoma
Abstract
Introduction: Canine lymphoma (cL) is one of the most frequent cancers in dogs. The T-cell lymphoma (TcL) is not the most common phenotype but presents an aggressive behavior. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules which can circulate freely in blood or be associated with extracellular vesicles (EVs). The dysregulation of certain miRNAs has been identified in numerous types of human cancers and they have been largely investigated as possible tumors biomarkers in human medicine, while research in veterinary oncology is still scarce. The aim of this study was to compare the expression patterns of free circulating and EV-associated miRNAs in dogs with T-cell lymhoma (TcL) and healthy dogs.
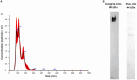
Methods: Eight dogs with TcL were selected as the lymphoma group (LG) and eight dogs were included as controls (Ctrl). Plasma samples were collected at the time of the diagnosis and EVs isolated with ultracentrifugation. miRNAs were extracted from both the circulating EVs and the plasma supernatant, obtaining EV-associated and free-miRNAs. Quantitative real-time PCR was performed to analyze the expression of 88 target miRNAs.
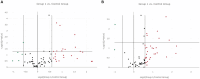
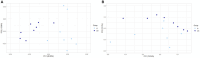
Results: Ten and seven differentially expressed miRNAs between LG and Ctrl were detected in EV-associated and free-miRNAs, respectively. Among EV-associated and free-miRNAs, only has-miR-222-3p was overexpressed in both conditions.
Discussion: All the differentially expressed miRNAs detected in this study, have been already described as dysregulated in other human or canine cancers. The EV-associated miRNAs, which appear to be more stable and better conserved than free-miRNAs, could be investigated in further larger studies to better assess their use as possible biomarkers for TcL.
Keywords: canine lymphoma; extracellular vesicles; liquid biopsy; miRNA; veterinary oncology.
Copyright © 2024 Capuano, Moccia, Molinari, Torrigiani, Ferro, Ferraresso, Bonsembiante, Leo and Zappulli.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

