Conserved regulatory motifs in the juxtamembrane domain and kinase N-lobe revealed through deep mutational scanning of the MET receptor tyrosine kinase domain
- PMID: 39268701
- PMCID: PMC11398868
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.91619
Conserved regulatory motifs in the juxtamembrane domain and kinase N-lobe revealed through deep mutational scanning of the MET receptor tyrosine kinase domain
Abstract
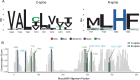
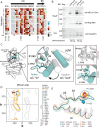
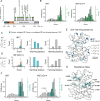
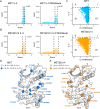
MET is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) responsible for initiating signaling pathways involved in development and wound repair. MET activation relies on ligand binding to the extracellular receptor, which prompts dimerization, intracellular phosphorylation, and recruitment of associated signaling proteins. Mutations, which are predominantly observed clinically in the intracellular juxtamembrane and kinase domains, can disrupt typical MET regulatory mechanisms. Understanding how juxtamembrane variants, such as exon 14 skipping (METΔEx14), and rare kinase domain mutations can increase signaling, often leading to cancer, remains a challenge. Here, we perform a parallel deep mutational scan (DMS) of the MET intracellular kinase domain in two fusion protein backgrounds: wild-type and METΔEx14. Our comparative approach has revealed a critical hydrophobic interaction between a juxtamembrane segment and the kinase ⍺C-helix, pointing to potential differences in regulatory mechanisms between MET and other RTKs. Additionally, we have uncovered a β5 motif that acts as a structural pivot for the kinase domain in MET and other TAM family of kinases. We also describe a number of previously unknown activating mutations, aiding the effort to annotate driver, passenger, and drug resistance mutations in the MET kinase domain.
Keywords: allostery; cancer; cancer biology; deep mutational scanning; human; molecular biophysics; mouse; receptor tyrosine kinase; structural biology; viruses.
© 2023, Estevam et al.
Conflict of interest statement
GE, EL, CM, CE, JM, WC, EC No competing interests declared, NJ E.A.C. is a consultant at IHP Therapeutics, Valar Labs, Tatara Therapeutics and Pear Diagnostics, reports receiving commercial research grants from Pfizer, and has stock ownership in Tatara Therapeutics, HDT Bio, Clara Health, Aqtual, and Guardant Health, JF N.J. is a founder of Rezo Therapeutics and a shareholder of Rezo Therapeutics, Sudo Therapeutics, and Type6 Therapeutics. N.J. is a SAB member of Sudo Therapeutics, Type6 Therapeutic and NIBR Oncology. The Jura laboratory has received sponsored research support from Genentech, Rezo Therapeutics and Type6 Therapeutics
Figures










Update of
-
Conserved regulatory motifs in the juxtamembrane domain and kinase N-lobe revealed through deep mutational scanning of the MET receptor tyrosine kinase domain.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 6:2023.08.03.551866. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.03.551866. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2024 Sep 13;12:RP91619. doi: 10.7554/eLife.91619. PMID: 37577651 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Abella JV, Peschard P, Naujokas MA, Lin T, Saucier C, Urbé S, Park M. Met/Hepatocyte growth factor receptor ubiquitination suppresses transformation and is required for Hrs phosphorylation. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2005;25:9632–9645. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.21.9632-9645.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahler E, Register AC, Chakraborty S, Fang L, Dieter EM, Sitko KA, Vidadala RSR, Trevillian BM, Golkowski M, Gelman H, Stephany JJ, Rubin AF, Merritt EA, Fowler DM, Maly DJ. A combined approach reveals a regulatory mechanism coupling src’s kinase activity, localization, and phosphotransferase-independent functions. Molecular Cell. 2019;74:393–408. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.02.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andrews S. FastQC: A quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. Version 0.12.0Babraham Bioinformatics. 2010 https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/
-
- Bardelli A, Longati P, Gramaglia D, Basilico C, Tamagnone L, Giordano S, Ballinari D, Michieli P, Comoglio PM. Uncoupling signal transducers from oncogenicMETmutants abrogates cell transformation and inhibits invasive growth. PNAS. 1998;95:14379–14383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.24.14379. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

