Nanotechnology-assisted combination drug delivery: a progressive approach for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 39268925
- PMCID: PMC11497954
- DOI: 10.1080/20415990.2024.2394012
Nanotechnology-assisted combination drug delivery: a progressive approach for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a heterogeneous hematopoietic cancer prevalent in adults, has been a leading cause of leukemia-associated deaths for decades. Despite advancements in understanding its pathology and pharmacological targets, therapeutic strategies have seen minimal change. The standard treatment, combining cytarabine and anthracycline, has persisted, accompanied by challenges such as pharmacokinetic issues and non-specific drug delivery, leading to severe side effects. Nanotechnology offers a promising solution through combination drug delivery. FDA-approved CPX351 (VYXEOS™) a liposomal formulation delivering doxorubicin and cytarabine, exemplifies enhanced therapeutic efficacy. Ongoing research explores various nanocarriers for delivering multiple bioactives, addressing drug targeting, pharmacokinetics and chemoresistance. This review highlights nanotechnology-based combination therapies for the effective management of AML, presenting a potential breakthrough in leukemia.
Keywords: acute myeloid leukemia; combination delivery; nanoparticles; nanotechnology; targeted delivery.
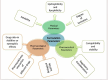
Plain language summary
[Box: see text].
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests or relevant affiliations with any organization or entity with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, stock ownership or options and expert testimony.
Figures



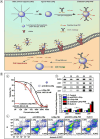
References
-
- Li J, Tang B, Miao Y, et al. Targeting of STAT5 using the small molecule topotecan hydrochloride suppresses acute myeloid leukemia progression. Oncol Rep. 2023;50(6):208. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8507 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
• This reference is of considerable interest as it highlights a specific small molecule approach targeting STAT5, a crucial pathway in AML progression.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
