In office sampling of eosinophil peroxidase to diagnose eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis
- PMID: 39269218
- PMCID: PMC11697230
- DOI: 10.1002/alr.23448
In office sampling of eosinophil peroxidase to diagnose eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis
Abstract
Background: Practical biomarkers for endotypic characterization of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) remain elusive, hindering clinical utility. Eosinophil peroxidase (EPX) is an enzyme released by activated eosinophils. The objective of this study was to evaluate a clinic EPX assay as a marker of eosinophilic CRS.
Methods: Subjects with and without CRS presenting to a tertiary care rhinology clinic were prospectively enrolled, and nasal cytology brushings were collected from the middle meatus during in-clinic nasal endoscopy. ELISA assay was used to quantify EPX levels, and a customized multiplex immunoassay was used to quantify inflammatory cytokine mediators. Findings were correlated with clinical data.
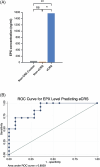
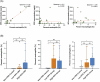
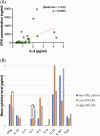
Results: Forty-two subjects were enrolled, including 31 CRS subjects and 11 controls. Median EPX levels were 125.0 ng/mL (standard deviation [SD] 1745.8) and 6.5 ng/mL (SD 99.0) for CRS group and controls, respectively (p = 0.003). EPX levels were associated with history of asthma (p = 0.015), allergies (p = 0.028), polyps (p = 0.0006), smell loss (p = 0.006), and systemic eosinophilia or elevated immunoglobulin E (p ≤ 0.0001). Twenty-eight subjects from both the CRS and control groups had prior pathology for comparison, with histologic confirmation of local tissue eosinophilia (>10 eosinophils/hpf) in 11 subjects. This subgroup had a median EPX level of 967.5 ng/mL compared to 10.6 ng/mL in 17 subjects without local tissue eosinophilia (p = 0.0008). EPX levels were positively correlated to interleukin-5 levels (p = 0.0005).
Conclusion: EPX levels can be measured via well-tolerated in-clinic collection of nasal mucus. EPX levels are associated with clinical markers of type 2 inflammation and tissue eosinophilia and may provide a valuable diagnostic tool to delineate eosinophilic CRS.
Keywords: chronic rhinosinusitis; endotype; eosinophil peroxidase; nasal polyp; type 2 inflammation.
© 2024 The Author(s). International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Academy of Otolaryngic Allergy and American Rhinologic Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Eosinophil Peroxidase: A Biomarker for Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis Agnostic of Polyp Status.Laryngoscope. 2024 Jan;134(1):69-78. doi: 10.1002/lary.30787. Epub 2023 May 31. Laryngoscope. 2024. PMID: 37255054 Free PMC article.
-
An eosinophil peroxidase activity assay accurately predicts eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023 Aug;152(2):400-407. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.04.012. Epub 2023 May 4. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37148919 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and cellular staging for the severity of chronic rhinosinusitis.Laryngoscope. 2004 Nov;114(11):1895-905. doi: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000147917.43615.c0. Laryngoscope. 2004. PMID: 15510011
-
Systemic biomarkers of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020 Feb;20(1):23-29. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000602. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31688152 Review.
-
Inflammatory and homeostatic roles of eosinophil subpopulations in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp pathogenesis.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 11;16:1568541. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1568541. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40292285 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endotyping in Chronic Rhinosinusitis-An EAACI Task Force Report.Allergy. 2025 Jan;80(1):132-147. doi: 10.1111/all.16418. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Allergy. 2025. PMID: 39641584 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

