Association of Resilience-Related Life Experiences on Variability on Age of Onset in Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Disease
- PMID: 39270149
- PMCID: PMC11399067
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000209766
Association of Resilience-Related Life Experiences on Variability on Age of Onset in Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Disease
Abstract
Background and objectives: It remains unknown whether the associations between protective lifestyles and sporadic dementia risk reported in observational studies also affect age at symptom onset (AAO) in autosomal dominant Alzheimer disease (ADAD) with predominant genetic influences. We investigated the associations between resilience-related life experiences and interindividual AAO variability in ADAD.
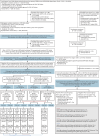
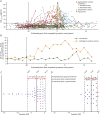
Methods: We performed a longitudinal and confirmatory analysis of the Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network prospective observational cohort (January 2009-June 2018, follow-up duration 2.13 ± 2.22 years), involving clinical, CSF, and lifestyle/behavioral assessments. We performed a 2-pronged comprehensive resilience assessment in each cohort. Cohort 1, incorporating the general resilience definition (cognitive maintenance [Clinical Dementia Rating = 0] despite high pathology), included carriers during the periods of significant CSFp-tau181 variability and grouped into resilience/resistance outcome bins according to the dichotomous pathologic and cognitive statuses, subcategorized by the estimated years from expected symptom onset (EYO). Cohort 2, focused on ADAD-specific genetically determined time frame characterizing the onset predictability, included asymptomatic participants with available preclinical lifestyle data and AAO outcomes and grouped into delayed or earlier AAO relative to the parental AAO. Associations of cognitive, CSFp-tau181, and lifestyle/behavioral predictors with binary outcomes were investigated using logistic regression.
Results: Of 320 carriers (age 38.19 ± 10.94 years, female 56.25%), cohort 1 included 218 participants (39.00 ± 9.37 years, 57.34%) and cohort 2 included 28 participants (43.34 ± 7.40 years, 71.43%). In cohort 1, 218 carriers after -20 EYO, when the interindividual variability (SD) of CSFp-tau181 first became more than twice greater in carriers than in noncarriers, were grouped into low-risk control (asymptomatic, low pathology, n = 103), high-resilience (asymptomatic despite high pathology, n = 60), low-resilience (symptomatic despite low pathology, n = 15), and susceptible control (symptomatic, high pathology, n = 40) groups. Multivariable predictors of high resilience, controlling for age and depression, included higher conscientiousness (odds ratio 1.051 [95% CI 1.016-1.086], p = 0.004), openness to experience (1.068 [1.005-1.135], p = 0.03) (vs. susceptible controls), and agreeableness (1.082 [1.015-1.153], p = 0.02) (vs. low resilience). From 1 to 3 years before parental AAO (cohort 2), the multivariable predictor of delayed AAO, controlling for CSFp-tau181, was higher conscientiousness (0.916 [0.845-0.994], p = 0.036).
Discussion: Among the cognitively and socially integrated life experiences associated with resilience, measures of conscientiousness were useful indicators for evaluating resilience and predicting future dementia onset in late preclinical ADAD.
Conflict of interest statement
H.J. Son and J.S. Kim report no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. R.J. Bateman has received research funding from the National Institute on Aging (NIA; UFAG032438 [DIAN - grant], R01AG068319 [DIAN-TU Next Generation Tau Trial - grant], UFAG032438 [DIAN - grant], RF1AG061900 [Blood Ab- grant], R56AG061900 [Blood Ab- grant], R21AG067559 [NfL - grant], and R01AG53627/R56AG53627 [DIAN-TU Next Generation Prevention Trial - Research Grant]), the Alzheimer's Association (DIAN-TU-OLE-21-725093 [DIAN-TU Open Label Extension - grant], DIAN-TU-Tau-21-822987 [DIAN-TU Tau Next Generation - grant], Biogen [Tau SILK Consortium member, NfL Consortium member], AbbVie [Tau SILK Consortium member, NfL Consortium member], Bristol Meyer Squibbs [NfL Consortium member], Novartis [Tau SILK Consortium member], NINDS/NIA R01NS095773 [CNS Tau - grant], Investigator Initiated Research Grants for Centene Corporation, Rainwater Foundation, Assn for Frontotemporal Degeneration FTD Biomarkers Initiative, Biogen, BrightFocus Foundation, Cure Alzheimer's Fund, Coins for Alzheimer's Research Trust Fund, Eisai, The Foundation for Barnes-Jewish Hospital, TargetALS, Good Ventures Foundation, DIAN-TU Pharma Consortium [active: Eli Lilly and Company/Avid Radiopharmaceuticals, Hoffman-La Roche/Genentech, Biogen, Eisai, Janssen; previous: Abbvie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Forum, Mithridion, Novartis, Pfizer, United Neuroscience, Sanofi], Eli Lilly and Company [Tau SILK Consortium Member], Hoffman-La Roche [receipt of drugs and services, NfL Consortium Member], CogState [in-kind support] and Signant [in-kind support]), outside of the submitted work. He has received royalties from C2N Diagnostics, lecture fees from Korean Dementia Association, American Neurological Association, Fondazione Prada, and Weill Cornell Medical College, supports for meeting or travel from Hoffman-La Roche, Alzheimer's Association Roundtable, Duke Margolis Alzheimer's Roundtable, BrightFocus Foundation, Tau Consortium Investigator's Meeting, Fondazione Prada and NAPA Advisory Council on Alzheimer's Research and drugs and services from Eisai (DIAN-TU Next Generation Trial), Janssen (DIAN-TU Next Generation Trial) and Hoffman-La Roche (DIAN-TU Open Label Extension - Gantenerumab), outside of the submitted work. He has served as a Data Safety Monitoring Board for Hoffman-La Roche/Genentech, Biogen - Combination therapy for Alzheimer's disease, UK Dementia Research Institute at University College London, Stanford University, and Next Generation Translational Proteomics for Alzheimer's and Related Dementias and the scientific advisory board for C2N Diagnostics, outside of the submitted work. He has patents (Washington University w/RJB as coinventor) titled “Methods for Measuring the Metabolism of CNS Derived Biomolecules In Vivo” (US nonprovisional patent application 12/267,974), “Methods for Measuring the Metabolism of neurally Derived Biomolecules in vivo” (US nonprovisional patent application 13/005,233), “Plasma based methods for detecting CNS Amyloid Disposition” (US nonprovisional patent application 62/492,718), “Plasma based methods for determining A-Beta Amyloidosis” (US nonprovisional patent application 16/610,428), “Methods of Treating Based on site-specific tau phosphorylation” (US nonprovisional patent application 17/015,985) and “Tau Kinetic Measurements” (US nonprovisional patent application 15/515,909), outside of the submitted work. S. Kim, J.J. Llibre-Guerra, G.S. Day, J. Chhatwal, and S.B. Berman report no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. P.R. Schofield has received research funding from the NIH, Anonymous Foundation, Roth Charitable Foundation, NHMRC (Australia), MRFF (Australia) and NSW Health, outside of the submitted work. He has served as chief executive officer for Neuroscience Research Australia, company director for Neuroscience Research Australia Foundation, The Health-Science Alliance, Australian Association of Medical Research Institutes, the Australian Dementia Network (ADNeT) Ltd, and StandingTall Pty Ltd, company director/chief executive officer for Schizophrenia Research Institute, president for Australasian Neuroscience Society, member/steering committee for Maridulu Budyari Gumal - Sydney Partnership for Health Education, Research and Enterprise (SPHERE), chair/national medical advisory panel for The Judith Jane Mason & Harold Stannett Williams Memorial Foundation and ambassador for Business Events Sydney, outside of the submitted work. M. Jucker reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. J. Levin has received research funding from the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE) and consulting fees from Axon Neuroscience and Biogen, lecture fees from Biogen, Bayer Vital, and Roche, author fees from Thieme medical publishers and W. Kohlhammer GmbH medical publishers, and support for attending meetings from AbbVie and Biogen, outside of the submitted work. He has a pending patent, titled “Pharmaceutical Composition and Methods of Use (EP 22 159 408.8),” filed by MODAG GmbH, and has served as a Data Safety Monitoring Board for Axon Neuroscience and as a part-time CMO for MODAG GmbH, outside of the submitted work. J.H. Lee reports no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. R.J. Perrin and J.C. Morris have received research funding from the NIH (U19 AG032438). J.C. Morris has received research funding from the NIH (P30 AG066444, P01AG003991, P01AG026276), consulting fees from Barcelona Brain Research Center (BBRC) and Native Alzheimer Disease-Related Resource Center in Minority Aging Research (Ext Adv Board) and lecture fees from Montefiore Grand Rounds (NY) and Tetra-Inst ADRC seminar series (Grand Rds, NY), outside of the submitted work. He has served as a Data Safety Monitoring Board for Cure Alzheimer's Fund (the Research Strategy Council), Diverse VCID Observational Study Monitoring Board, and LEADS Advisory Board (Indiana University), outside of the submitted work. C. Cruchaga, J. Hassenstab, S.P. Salloway, J.H. Lee, and A. Daniels report no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. Go to
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
