Atypical ductal or lobular hyperplasia, lobular carcinoma in-situ, flat epithelial atypia, and future risk of developing breast cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39270543
- PMCID: PMC11415589
- DOI: 10.1016/j.breast.2024.103807
Atypical ductal or lobular hyperplasia, lobular carcinoma in-situ, flat epithelial atypia, and future risk of developing breast cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Biopsy-proven breast lesions such as atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) or atypical lobular hyperplasia (ALH), lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) and flat epithelial atypia (FEA) increase subsequent risk of breast cancer (BC), but long-term risk has not been synthesized. A systematic review was conducted to quantify future risk of breast cancer accounting for time since diagnosis of these high-risk lesions.
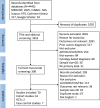
Methods: A systematic search of literature from 2000 was performed to identify studies reporting BC as an outcome following core-needle or excision biopsy histology diagnosis of ADH, ALH, LCIS, lobular neoplasia (LN) or FEA. Meta-analyses were conducted to estimate cumulative BC incidence at five-yearly intervals following initial diagnosis for each histology type.
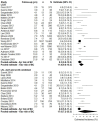
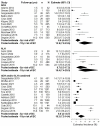
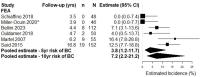
Results: Seventy studies reporting on 47,671 subjects met eligibility criteria. BC incidence at five years post-diagnosis with a high-risk lesion was estimated to be 9.3 % (95 % CI 6.9-12.5 %) for LCIS, 6.6 % (95 % CI 4.4-9.7 %) for ADH, 9.7 % (95 % CI 5.3-17.2 %) for ALH, 8.6 % (95 % CI 6.5-11.4 %) for LN, and 3.8 % (95 % CI 1.2-11.7 %) for FEA. At ten years post-diagnosis, BC incidence was estimated to be 11.8 % (95 % CI 9.0-15.3 %) for LCIS, 13.9 % (95 % CI 7.8-23.6 %) for ADH, 15.4 % (95 % CI 7.2-29.3 %) for ALH, 17.0 % (95 % CI 7.2-35.3 %) for LN and 7.2 % (95 % CI 2.2-21.2 %) for FEA.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate increased BC risk sustained over time since initial diagnosis of high-risk breast lesions, varying by lesion type, with relatively less evidence for FEA.
Keywords: Atypical proliferations; Biopsy; Breast cancer; Breast cancer risk; Lobular carcinoma in-situ; Mammography.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R.L., et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Heer E., Harper A., Escandor N., et al. Global burden and trends in premenopausal and postmenopausal breast cancer: a population-based study. Lancet Glob Health. 2020;8(8):e1027–e1037. - PubMed
-
- Hartmann L.C., Sellers T.A., Frost M.H., et al. Benign breast disease and the risk of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(3):229–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

