DrugMAP 2.0: molecular atlas and pharma-information of all drugs
- PMID: 39271119
- PMCID: PMC11701670
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae791
DrugMAP 2.0: molecular atlas and pharma-information of all drugs
Abstract
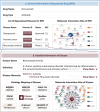
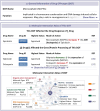
The escalating costs and high failure rates have decelerated the pace of drug development, which amplifies the research interests in developing combinatorial/repurposed drugs and understanding off-target adverse drug reaction (ADR). In other words, it is demanded to delineate the molecular atlas and pharma-information for the combinatorial/repurposed drugs and off-target interactions. However, such invaluable data were inadequately covered by existing databases. In this study, a major update was thus conducted to the DrugMAP, which accumulated (a) 20831 combinatorial drugs and their interacting atlas involving 1583 pharmacologically important molecules; (b) 842 repurposed drugs and their interacting atlas with 795 molecules; (c) 3260 off-targets relevant to the ADRs of 2731 drugs and (d) various types of pharmaceutical information, including diverse ADMET properties, versatile diseases, and various ADRs/off-targets. With the growing demands for discovering combinatorial/repurposed therapies and the rapidly emerging interest in AI-based drug discovery, DrugMAP was highly expected to act as an indispensable supplement to existing databases facilitating drug discovery, which was accessible at: https://idrblab.org/drugmap/.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
DrugMAP: molecular atlas and pharma-information of all drugs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D1288-D1299. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac813. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36243961 Free PMC article.
-
DrugMap Central: an on-line query and visualization tool to facilitate drug repositioning studies.Bioinformatics. 2013 Jul 15;29(14):1834-6. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt279. Epub 2013 May 15. Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23681121 Free PMC article.
-
INTEDE 2.0: the metabolic roadmap of drugs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jan 5;52(D1):D1355-D1364. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 37930837 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting targeted polypharmacology for drug repositioning and multi- target drug discovery.Curr Med Chem. 2013;20(13):1646-61. doi: 10.2174/0929867311320130005. Curr Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23410165 Review.
-
Rational application of drug promiscuity in medicinal chemistry.Future Med Chem. 2018 Aug 1;10(15):1835-1851. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2018-0018. Epub 2018 Jul 18. Future Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30019924 Review.
Cited by
-
AI comes to the Nobel Prize and drug discovery.J Pharm Anal. 2024 Nov;14(11):101160. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101160. Epub 2024 Dec 21. J Pharm Anal. 2024. PMID: 39850961 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The 2025 Nucleic Acids Research database issue and the online molecular biology database collection.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jan 6;53(D1):D1-D9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1220. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39658041 Free PMC article.
-
SYNBIP 2.0: epitopes mapping, sequence expansion and scaffolds discovery for synthetic binding protein innovation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jan 6;53(D1):D595-D603. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae893. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39413165 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jin H., Wang L., Bernards R.. Rational combinations of targeted cancer therapies: background, advances and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2023; 22:213–234. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82373790/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- LR21H300001/Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province
- 2018QNA7023/Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities
- 2022YFC3400501/National Key R&D Program of China
- 181201*194232101/Double Top-Class University
- 2020C03010/Key R&D Program of Zhejiang
- Westlake Laboratory (Westlake Lab of Life Sciences and Biomedicine)
- Leading Talent of the 'Ten Thousand Plan' National High-Level Talents Special Support Plan of China
- Alibaba-Zhejiang University Joint Research Center of Future Digital Healthcare
- Zhejiang University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

