Whole Body Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model to Explain A Patient With Drug-Drug Interaction Between Voriconazole and Flucloxacillin
- PMID: 39271639
- PMCID: PMC11549138
- DOI: 10.1007/s13318-024-00916-1
Whole Body Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model to Explain A Patient With Drug-Drug Interaction Between Voriconazole and Flucloxacillin
Abstract
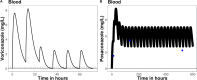
Background and objectives: Voriconazole administered concomitantly with flucloxacillin may result in subtherapeutic plasma concentrations as shown in a patient with Staphylococcus aureus sepsis and a probable pulmonary aspergillosis. After switching our patient to posaconazole, therapeutic concentrations were reached. The aim of this study was to first test our hypothesis that flucloxacillin competes with voriconazole not posaconazole for binding to albumin ex vivo, leading to lower total concentrations in plasma.
Methods: A physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model was then applied to predict the mechanism of action of the drug-drug interaction (DDI). The model included non-linear hepatic metabolism and the effect of a severe infectious disease on cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes activity.
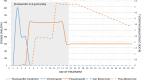
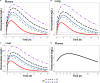
Results: The unbound voriconazole concentration remained unchanged in plasma after adding flucloxacillin, thereby rejecting our hypothesis of albumin-binding site competition. The PBPK model was able to adequately predict the plasma concentration of both voriconazole and posaconazole over time in healthy volunteers. Upregulation of CYP3A4, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19 through the pregnane X receptor (PXR) gene by flucloxacillin resulted in decreased voriconazole plasma concentrations, reflecting the DDI observations in our patient. Posaconazole metabolism was not affected, or was only limitedly affected, by the changes through the PXR gene, which agrees with the observed plasma concentrations within the target range in our patient.
Conclusions: Ex vivo experiments reported that the unbound voriconazole plasma concentration remained unchanged after adding flucloxacillin. The PBPK model describes the potential mechanism driving the drug-drug and drug-disease interaction of voriconazole and flucloxacillin, highlighting the large substantial influence of flucloxacillin on the PXR gene and the influence of infection on voriconazole plasma concentrations, and suggests a more limited effect on other triazoles.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interaction between posaconazole and flucloxacillin in a lung transplant patient: decrease in plasma exposure of posaconazole and possible undertreatment of invasive aspergillosis: case report.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Mar 27;22(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-01904-4. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 35346142 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between voriconazole and flucloxacillin during treatment of disseminated Scedosporium apiospermum infection.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2015 Jul;70(7):2171-3. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkv069. Epub 2015 Mar 15. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25777322 No abstract available.
-
Interaction between flucloxacillin and azoles: Is isavuconazole next?Mycoses. 2021 Dec;64(12):1508-1511. doi: 10.1111/myc.13373. Epub 2021 Oct 9. Mycoses. 2021. PMID: 34553797
-
[Drug-drug interaction of antifungal drugs].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2005 Oct;125(10):795-805. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.125.795. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2005. PMID: 16205037 Review. Japanese.
-
Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic profile of voriconazole.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2006;45(7):649-63. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200645070-00002. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2006. PMID: 16802848 Review.
References
-
- Voriconazole: National Library of Medicine. MedlinePlus [Internet]. Medlineplus.gov. [cited 2024 Aug 12]. Available from: https://medlineplus.gov/
-
- Flucloxacillin 500mg Capsules - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) - Homepage [Internet]. European Medicines Agency (EMA). [cited 2024 Aug 12]. Available from: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/homepage
-
- Kennedy B, Larcombe R, Chaptini C, Gordon DL. Interaction between voriconazole and flucloxacillin during treatment of disseminated Scedosporiumapiospermum infection. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2015;70(7):2171–3. 10.1093/jac/dkv069. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

