Development of nanocomposite-selenium filter for water disinfection and bioremediation of wastewater from Hg and AgNPs
- PMID: 39271750
- PMCID: PMC11399127
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-70120-3
Development of nanocomposite-selenium filter for water disinfection and bioremediation of wastewater from Hg and AgNPs
Abstract
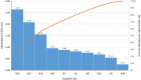
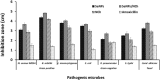
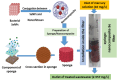
Selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) are used in several sectors as antitumor, antimicrobial, and environmental adsorbents. Thus, the present research objective was the production of bacterial-SeNPs as an active and environmentally-friendly antibacterial and adsorbent agents and application into novel nanocomposite filter. From a total of 25 samples (soil, wastewater, and water) obtained from different locations in Egypt, 60 selenium-resistant bacterial isolates were obtained (on a mineral salt medium supplemented with selenium ions). After screening (based on the conversion of selenium from ionic form to nanoform), a superior bacterial isolate for SeNPs formation was obtained and molecular identified as Bacillus pumilus isolate OR431753. The high yield of SeNPs was noted after optimization (glucose as carbon source, pH 9 at 30 °C). The produced SeNPs were characterized as approximately 15 nm-diameter spherical nanoparticles, in addition to the presence of organic substances around these particles like polysaccharides and aromatic amines (protein residues). Also, they have antibacterial activity increased after formation of nanocomposite with nano-chitosan (SeNPs/NCh) against several pathogens. The antibacterial activity (expressed as a diameter of the inhibitory zone) averaged between 2.1 and 4.3, 2.7 and 4.8 cm for SeNPs and SeNPs/NCh, respectively compared with 1.1 to 1.8 cm for Amoxicillin. The produced nanoselenium/chitosan was used as a biofilter to remove mercury (Hg) and AgNPs as model chemicals with serious toxicity and potential pollutant for water bodies in many industries. The new SeNPs/NCh biofilter has proven highly effective in individually removing mercury and AgNPs from their synthetic wastewaters, with an efficiency of up to 99%. Moreover, the removal efficiency of AgNPs stabilized at 99% after treating them with the syringe filter-Se nanocomposite for 4 cycles of treatment (5 min each).
Keywords: Bacillus pumilus; Heavy metals removal; Nanochitosan; Polysaccharide; SeNPs biosynthesis; SeNPs/NCh biofilter.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Zaynab, M. et al. Health and environmental effects of heavy metals. J. King Saud Univ. Sci.34(1), 101653. 10.1016/j.jksus.2021.101653 (2022).10.1016/j.jksus.2021.101653 - DOI
-
- Khan, I., Saeed, K. & Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem.12(7), 908–931. 10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011 (2019).10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011 - DOI
-
- Samuel, M. S., Selvarajan, E., Chidambaram, R., Patel, H. & Brindhadevi, K. Clean approach for chromium removal in aqueous environments and role of nanomaterials in bioremediation: Present research and future perspective. Chemosphere284, 131368. 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131368 (2021). 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131368 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shalaby, M. A., Matter, I. A., Gharieb, M. M. & Darwesh, O. M. Biosorption performance of the multi-metal tolerant fungus Aspergillus sp. for removal of some metallic nanoparticles from aqueous solutions. Heliyon9(5), e16125. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16125 (2023). 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16125 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

