Assessing health-related quality of life in patients with interstitial lung diseases
- PMID: 39272068
- PMCID: PMC11401309
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-024-03262-9
Assessing health-related quality of life in patients with interstitial lung diseases
Abstract
Background: The R-Scale-PF was proposed to evaluate the health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). We generated a German version of the R-Scale-PF (GR-Scale), representing the first translation of the questionnaire into another language and assessed HRQoL longitudinally in various interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) using the R-Scale-PF scoring system at a specialized ILD centre.
Methods: We have translated the questionnaire in accordance with the WHO translation guidelines and applied it to 80 ILD patients of our department, with follow-ups after 3-6 months, assessing its internal consistency, floor and ceiling effects, concurrent validity, known-groups validity, and its responsiveness to changes over time.
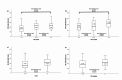
Results: At baseline, all 80 patients completed the GR-Scale. In 70 patients (87.5%), follow-up data could be obtained after 4.43 ± 1.2 months. The GR-Scale demonstrated acceptable internal consistency (Cronbach's α 0.749) and slight floor effects. Concurrent validity analysis showed weak but significant correlations with forced vital capacity (FVC; r=-0.282 p = 0.011) and diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide (DLco; r=-0.254 p = 0.025). In the follow-up analysis, moderate correlations were found with FVC (r=-0.41 p < 0.001) and DLco (r=-0.445 p < 0.001). No significant difference in the total score was found between patients with IPF (n = 10) and with non-IPF ILDs (n = 70). The GR-Scale successfully discriminated between groups of varying disease severity based on lung function parameters and the need for long-term oxygen therapy (LTOT). Furthermore, it was able to distinguish between patients showing improvement, stability or decline of lung function parameters.
Conclusion: Our prospective observational pilot study suggests that the GR-Scales is a simple and quick tool to measure HRQoL in patients with ILDs, thus providing an important additional information for the clinical assessment of ILD patients.
Trial registration: Our study was retrospectively registered in the German Clinical Trial Register (DRKS) on 02.11.2022 (DRKS-ID: DRKS00030599).
Keywords: HRQoL; Health related quality of life; ILD; IPF; Interstitial lung disease; Survey.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
SS received support from the Chiesi GmbH for travel and participation in the ERS International Congress 2023. KM received speaker honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim, unrelated to the current manuscript. AL received support from the MSD Sharp & Dohme GmbH for attending a training course and from the AOP Orphan Pharmaceuticals Germany GmbH for travel and participation in a scientific meeting, unrelated to the current manuscript. GL, TK, JG, TV, NK, JB do not have competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Translation to Spanish and Validation of the Specific Saint George's Questionnaire for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Arch Bronconeumol (Engl Ed). 2018 Feb;54(2):68-73. doi: 10.1016/j.arbres.2017.09.004. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Arch Bronconeumol (Engl Ed). 2018. PMID: 29102341 English, Spanish.
-
Monthly pulse methylprednisolone infusions in patients with non-idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis interstitial lung diseases: a single-center retrospective analyses.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2025 Jan-Dec;19:17534666251342661. doi: 10.1177/17534666251342661. Epub 2025 May 30. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2025. PMID: 40444328 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the King's Brief Interstitial Lung Disease questionnaire in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.BMC Pulm Med. 2019 Dec 19;19(1):255. doi: 10.1186/s12890-019-1018-0. BMC Pulm Med. 2019. PMID: 31856786 Free PMC article.
-
The burden of cough in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and other interstitial lung diseases: a systematic evidence synthesis.Respir Res. 2024 Aug 27;25(1):325. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02897-w. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39192278 Free PMC article.
-
A cohort study of Danish patients with interstitial lung diseases: burden, severity, treatment and survival.Dan Med J. 2015 Apr;62(4):B5069. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 25872544 Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

