The current status and influencing factors of oral frailty in elderly maintenance hemodialysis patients based on the Andersen Oral Health Outcome Model
- PMID: 39272094
- PMCID: PMC11401281
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-024-04872-9
The current status and influencing factors of oral frailty in elderly maintenance hemodialysis patients based on the Andersen Oral Health Outcome Model
Abstract
Objectives: To analyse the elements that influence oral frailty in elderly maintenance hemodialysis patients and to comprehend the present state of this condition.
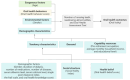
Methods: A survey of 325 elderly maintenance hemodialysis patients from three hospitals in Huzhou City was conducted using a general information questionnaire, the Oral Health Assessment Tool, the Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice of Oral Health Questionnaire, the Social Frailty, the Frail Scale, and the Oral Frailty Index.
Results: In elderly maintenance hemodialysis patients, the prevalence of oral frailty was 45.2%. Factors influencing it include the Oral Health Knowledge Score (OR = 0.84, 95% CI 0.72-0.98), Oral Health Behavior Score (OR = 0.95, 95% CI 0.92-0.98), insufficient dialysis (OR = 0.30, 95% CI 0.14-0.63), social frailty (OR = 3.72, 95% CI 1.57-8.83), physical frailty (OR = 3.12, 95% CI 1.55-6.30), number of missing teeth (OR = 1.09, 95% CI 1.03-1.15), swallowing abnormalities (OR = 2.84, 95% CI 1.26-6.38), and oral health scores (OR = 1.34, 95% CI 1.14-1.57) (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Patients on elderly maintenance hemodialysis are more susceptible to oral frailty. Nursing staff should develop scientifically sound, effective, and targeted oral management strategies for these patients.
Keywords: Elderly; Maintenance hemodialysis; Oral frailty; Risk factor.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Wang SZ, Zhu YJ, Tang WZ, Liu N, Ye F, Li GQ, et al. Meta analysis of the prevalence of chronic kidney disease in adult and elderly populations in China[J]. Chin J Gerontol. 2017;37(21):5384–8.
-
- He B, Zhang W, Liu L, Wang H, Zou YW, Jiang YX, et al. Renal cell carcinoma in patients with end⁃stage renal disease: a clinicopathological analysis[J]. Chin J Pathol. 2019;48(11):846–50. - PubMed
-
- Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, Newman AB, Hirsch C, Gottdiener J, et al. Frailty in older adults: evidence for a phenotype[J]. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001;56(3):M146–M. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical