The Promising Role of Synthetic Flavors in Advancing Fish Feeding Strategies: A Focus on Adult Female Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Growth, Welfare, Appetite, and Reproductive Performances
- PMID: 39272373
- PMCID: PMC11394377
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14172588
The Promising Role of Synthetic Flavors in Advancing Fish Feeding Strategies: A Focus on Adult Female Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Growth, Welfare, Appetite, and Reproductive Performances
Abstract
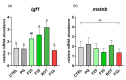
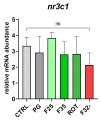
The present study aimed to test over a six-month period different synthetic flavors in zebrafish (Danio rerio) as an experimental model. Specifically, two attractive and one repulsive synthetic flavors were added (1% w/w) to a specific zebrafish diet, which was administered to the fish during the whole life cycle (from larvae to adults), to evaluate their physiological responses, emphasizing fish welfare, feed intake, growth, reward mechanisms, and reproductive performances. Fish welfare was not affected by all tested flavors, while both attractive flavors promoted fish feed ingestion and growth. The results were supported by both molecular and immunohistochemical analyses on appetite-regulating neurohormonal signals, along with the influence of the feed hedonic properties induced by the brain reward sensation, as demonstrated by the dopamine receptor gene expression. Finally, the present study demonstrated that a higher feed intake also had positive implications on fish reproductive performances, suggesting a promising role of synthetic flavors for the aquaculture industry. In conclusion, the results highlighted the potential of synthetic flavors to improve fish feeding strategies by providing a consistent and effective alternative to traditional stimulants, thereby reducing dependence on natural sources.
Keywords: aquaculture; feed attractant; feed intake; histology; sustainable aquafeeds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures








References
-
- Chemello G., Zarantoniello M., Randazzo B., Gioacchini G., Truzzi C., Cardinaletti G., Riolo P., Olivotto I. Effects of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Enriched with Schizochytrium Sp. on Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Reproductive Performances. Aquaculture. 2022;550:737853. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737853. - DOI
-
- Moutinho S., Peres H., Serra C., Martínez-Llorens S., Tomás-Vidal A., Jover-Cerdá M., Oliva-Teles A. Meat and Bone Meal as Partial Replacement of Fishmeal in Diets for Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) Juveniles: Diets Digestibility, Digestive Function, and Microbiota Modulation. Aquaculture. 2017;479:721–731. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.07.021. - DOI
-
- Randazzo B., Zarantoniello M., Cardinaletti G., Cerri R., Giorgini E., Belloni A., Contò M., Tibaldi E., Olivotto I. Hermetia illucens and Poultry By-Product Meals as Alternatives to Plant Protein Sources in Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata) Diet: A Multidisciplinary Study on Fish Gut Status. Animals. 2021;11:677. doi: 10.3390/ani11030677. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zarantoniello M., Pulido Rodriguez L.F., Randazzo B., Cardinaletti G., Giorgini E., Belloni A., Secci G., Faccenda F., Pulcini D., Parisi G., et al. Conventional Feed Additives or Red Claw Crayfish Meal and Dried Microbial Biomass as Feed Supplement in Fish Meal-Free Diets for Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Possible Ameliorative Effects on Growth and Gut Health Status. Aquaculture. 2022;554:738137. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2022.738137. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

