AI-Enhanced ECG Applications in Cardiology: Comprehensive Insights from the Current Literature with a Focus on COVID-19 and Multiple Cardiovascular Conditions
- PMID: 39272624
- PMCID: PMC11394310
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14171839
AI-Enhanced ECG Applications in Cardiology: Comprehensive Insights from the Current Literature with a Focus on COVID-19 and Multiple Cardiovascular Conditions
Abstract
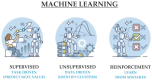
The application of artificial intelligence (AI) in electrocardiography is revolutionizing cardiology and providing essential insights into the consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic. This comprehensive review explores AI-enhanced ECG (AI-ECG) applications in risk prediction and diagnosis of heart diseases, with a dedicated chapter on COVID-19-related complications. Introductory concepts on AI and machine learning (ML) are explained to provide a foundational understanding for those seeking knowledge, supported by examples from the literature and current practices. We analyze AI and ML methods for arrhythmias, heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, mortality prediction, cardiomyopathy, mitral regurgitation, hypertension, pulmonary embolism, and myocardial infarction, comparing their effectiveness from both medical and AI perspectives. Special emphasis is placed on AI applications in COVID-19 and cardiology, including detailed comparisons of different methods, identifying the most suitable AI approaches for specific medical applications and analyzing their strengths, weaknesses, accuracy, clinical relevance, and key findings. Additionally, we explore AI's role in the emerging field of cardio-oncology, particularly in managing chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity and detecting cardiac masses. This comprehensive review serves as both an insightful guide and a call to action for further research and collaboration in the integration of AI in cardiology, aiming to enhance precision medicine and optimize clinical decision-making.
Keywords: COVID-19; artificial intelligence; cardio-oncology; cardiology; convolutional neural networks (CNNs); deep learning (DL); diagnosis; electrocardiography; machine learning (ML); risk prediction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Muzammil M.A., Javid S., Afridi A.K., Siddineni R., Shahabi M., Haseeb M., Fariha F.N.U., Kumar S., Zaveri S., Nashwan A.J. Artificial Intelligence-Enhanced Electrocardiography for Accurate Diagnosis and Management of Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Electrocardiol. 2024;83:30–40. doi: 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2024.01.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baek Y.-S. The Emergence and Clinical Significance of Artificial Intelligence–Enhanced Electrocardiography. Cardiovasc. Prev. Pharmacother. 2024;6:41–47. doi: 10.36011/cpp.2024.6.e7. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous