Identifying the Pathogenic Variants in Heart Genes in Vietnamese Sudden Unexplained Death Victims by Next-Generation Sequencing
- PMID: 39272661
- PMCID: PMC11394071
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14171876
Identifying the Pathogenic Variants in Heart Genes in Vietnamese Sudden Unexplained Death Victims by Next-Generation Sequencing
Abstract
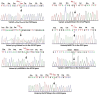
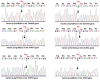
In forensics, one-third of sudden deaths remain unexplained after a forensic autopsy. A majority of these sudden unexplained deaths (SUDs) are considered to be caused by inherited cardiovascular diseases. In this study, we investigated 40 young SUD cases (<40 years), with non-diagnostic structural cardiac abnormalities, using Targeted NGS (next-generation sequencing) for 167 genes previously associated with inherited cardiomyopathies and channelopathies. Fifteen cases identified 17 variants on related genes including the following: AKAP9, CSRP3, GSN, HTRA1, KCNA5, LAMA4, MYBPC3, MYH6, MYLK, RYR2, SCN5A, SCN10A, SLC4A3, TNNI3, TNNI3K, and TNNT2. Of these, eight variants were novel, and nine variants were reported in the ClinVar database. Five were determined to be pathogenic and four were not evaluated. The novel and unevaluated variants were predicted by using in silico tools, which revealed that four novel variants (c.5187_5188dup, p.Arg1730llefsTer4 in the AKAP9 gene; c.1454A>T, p.Lys485Met in the MYH6 gene; c.2535+1G>A in the SLC4A3 gene; and c.10498G>T, p.Asp3500Tyr in the RYR2 gene) were pathogenic and three variants (c.292C>G, p.Arg98Gly in the TNNI3 gene; c.683C>A, p.Pro228His in the KCN5A gene; and c.2275G>A, p.Glu759Lys in the MYBPC3 gene) still need to be further verified experimentally. The results of our study contributed to the general understanding of the causes of SUDs. They provided a scientific basis for screening the risk of sudden death in family members of victims. They also suggested that the Targeted NGS method may be used to identify the pathogenic variants in SUD victims.
Keywords: Vietnamese victims; cardiac channelopathies; cardiomyopathies; molecular autopsy; next-generation sequencing (NGS); sudden unexplained death (SUD).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Next-generation sequencing of 34 genes in sudden unexplained death victims in forensics and in patients with channelopathic cardiac diseases.Int J Legal Med. 2015 Jul;129(4):793-800. doi: 10.1007/s00414-014-1105-y. Epub 2014 Dec 3. Int J Legal Med. 2015. PMID: 25467552
-
Exome analysis in 34 sudden unexplained death (SUD) victims mainly identified variants in channelopathy-associated genes.Int J Legal Med. 2018 Jul;132(4):1057-1065. doi: 10.1007/s00414-018-1775-y. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Int J Legal Med. 2018. PMID: 29350269
-
Targeted next generation sequencing application in cardiac channelopathies: Analysis of a cohort of autopsy-negative sudden unexplained deaths.Forensic Sci Int. 2015 Sep;254:5-11. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2015.06.023. Epub 2015 Jul 3. Forensic Sci Int. 2015. PMID: 26164358
-
Molecular Autopsy of Sudden Cardiac Death in the Genomics Era.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Jul 30;11(8):1378. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11081378. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34441312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of molecular autopsy in unexplained sudden cardiac death.Curr Opin Cardiol. 2006 May;21(3):166-72. doi: 10.1097/01.hco.0000221576.33501.83. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2006. PMID: 16601452 Review.
References
-
- Priori S.G., Blomstrom-Lundqvist C., Mazzanti A., Bloma N., Borggrefe M., Camm J., Elliott P.M., Fitzsimons D., Hatala R., Hindricks G., et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death the Task Force for the Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death of the Europea. Eur. Heart J. 2015;36:2793–2867. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv316. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous