Predicting Mortality in Sepsis: The Role of Dynamic Biomarker Changes and Clinical Scores-A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 39272757
- PMCID: PMC11393859
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14171973
Predicting Mortality in Sepsis: The Role of Dynamic Biomarker Changes and Clinical Scores-A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: The prognostic value of baseline inflammatory markers in sepsis remains controversial, with conflicting evidence regarding their association with mortality. The dynamic changes in these markers over time might offer additional insights into disease progression and patient outcomes.
Methods: This retrospective observational study included 138 patients with severe infections. The inflammatory biomarkers procalcitonin (PCT), C-reactive protein (CRP), and lactate (LAC) were measured at three time points: upon hospital admission (baseline), approximately 24-48 h after admission (second measurement; M2), and 48-72 h after admission (third measurement; M3). The primary outcome was 30-day mortality. A Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare the biomarker levels between the survivors and non-survivors. A Spearman's correlation was used to assess the relationships between the baseline parameters. A logistic regression and a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis were employed to evaluate the prognostic value of the baseline markers and their dynamic changes.
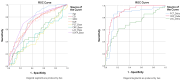
Results: The baseline LAC and SOFA score were significantly associated with 30-day mortality. The percentage decrease in PCT, CRP, and LAC from the baseline to M3 emerged as strong predictors of survival, with the ROC curve analysis demonstrating superior discriminatory ability compared to the baseline values. CRP_Delta exhibited the highest AUC (0.903), followed by PCT_Delta (0.843) and LAC_Delta (0.703).
Conclusions: The dynamic changes in these inflammatory biomarkers, particularly PCT, CRP, and LAC, offer valuable prognostic information beyond their baseline levels in predicting 30-day mortality in severe infections. These findings highlight the importance of monitoring biomarker trends for early risk stratification and potential treatment guidance.
Keywords: CRP; biomarkers; lactate; procalcitonin; prognosis; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rudd K.E., Johnson S.C., Agesa K.M., Shackelford K.A., Tsoi D., Kievlan D.R., Colombara D.V., Ikuta K.S., Kissoon N., Finfer S., et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 2020;395:200–211. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Evans L., Rhodes A., Alhazzani W., Antonelli M., Coopersmith C.M., French C., Machado F.R., Mcintyre L., Ostermann M., Prescott H.C., et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Crit. Care Med. 2021;49:e1063–e1143. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000005337. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous