Advancing Cancer Therapy: The Role of KIF20A as a Target for Inhibitor Development and Immunotherapy
- PMID: 39272816
- PMCID: PMC11393963
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16172958
Advancing Cancer Therapy: The Role of KIF20A as a Target for Inhibitor Development and Immunotherapy
Abstract
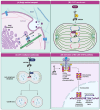
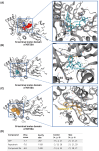
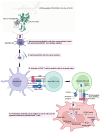
The analysis begins with a detailed examination of the gene expression and protein structure of KIF20A, highlighting its interaction with critical cellular components that influence key processes such as Golgi membrane transport and mitotic spindle assembly. The primary focus is on the development of specific KIF20A inhibitors, detailing their roles and the challenges encountered in enhancing their efficacy, such as achieving specificity, overcoming tumor resistance, and optimizing delivery systems. Additionally, it delves into the prognostic value of KIF20A across multiple cancer types, emphasizing its role as a novel tumor-associated antigen, which lays the groundwork for the development of targeted peptide vaccines. The therapeutic efficacy of these vaccines as demonstrated in recent clinical trials is discussed. Future directions are proposed, including the integration of precision medicine strategies to personalize treatments and the use of combination therapies to improve outcomes. By concentrating on the significant potential of KIF20A as both a direct target for inhibitors and an antigen in cancer vaccines, this review sets a foundation for future research aimed at harnessing KIF20A for effective cancer treatment.
Keywords: KIF20A; cancer; inhibitor; peptide vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional analysis of KIF20A, a potential immunotherapeutic target for glioma.J Neurooncol. 2017 Mar;132(1):63-74. doi: 10.1007/s11060-016-2360-1. Epub 2017 Jan 9. J Neurooncol. 2017. PMID: 28070829
-
Phase I/II clinical trial using HLA-A24-restricted peptide vaccine derived from KIF20A for patients with advanced pancreatic cancer.J Transl Med. 2013 Nov 16;11:291. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-11-291. J Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 24237633 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Expression, regulating mechanism and therapeutic target of KIF20A in multiple cancer.Heliyon. 2023 Jan 25;9(2):e13195. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13195. eCollection 2023 Feb. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36798768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles and mechanisms of Kinesin-6 KIF20A in spindle organization during cell division.Eur J Cell Biol. 2019 Jun;98(2-4):74-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2018.12.002. Epub 2018 Dec 16. Eur J Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30579662 Review.
-
A phase I clinical trial of vaccination with KIF20A-derived peptide in combination with gemcitabine for patients with advanced pancreatic cancer.J Immunother. 2014 Jan;37(1):36-42. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000012. J Immunother. 2014. PMID: 24316554 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Targeting Kinesins for Therapeutic Exploitation of Chromosomal Instability in Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Feb 18;17(4):685. doi: 10.3390/cancers17040685. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40002279 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

