Single-Port Extraperitoneal vs. Multiport Transperitoneal Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis
- PMID: 39272854
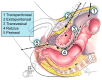
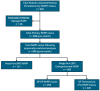
- PMCID: PMC11393968
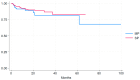
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16172994
Single-Port Extraperitoneal vs. Multiport Transperitoneal Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis
Abstract
(1) Background: Since the introduction of the purpose-built Single Port (SP) robotic platform, there has been an ongoing debate regarding its advantages compared to the established multi-port (MP) system. The goal of this present study is to compare the perioperative, oncological, and functional outcomes of SP Extraperitoneal robotic radical prostatectomy (RARP) versus that of MP Transperitoneal RARP approach at a high-volume tertiary center. (2) Methods: Based on a retrospective review of the prospectively maintained IRB-approved database, 925 patients successfully underwent RARP by a single experienced robotic surgeon. A 4:1 propensity-matched analysis based on the baseline prostate cancer International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Grade Group, clinical stage, and preoperative Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) was performed, which yielded a cohort of 606 patients-485 in the SP EP and 121 in the MP TP approaches. Of note, the SP EP approach also included the traditional Extraperitoneal (n = 259, 53.4%) and the novel Transvesical (TV) approaches (n = 226, 46.6%). (3) Results: The overall operative time was slightly longer in the SP cohort, with a mean of 198.9 min compared to 181.5 min for the MP group (p < 0.001). There were no intraoperative complications with the MP approach and only one during the SP approach. The SP EP technique demonstrated significant benefits, encompassing reduced intraoperative blood loss (SP 125.1 vs. MP 215.9 mL), shorter length of hospital stay (SP 12.6 vs. MP 31.9 h), reduced opioid use at the time of discharge (SP 14.4% vs. MP 85.1%), and an earlier Foley catheter removal (SP 6 vs. MP 8 days). From an oncological perspective, the rate of positive surgical margins remained comparable across both groups (p = 0.84). Regarding functional outcomes, the mean continence rates and Sexual Health Inventory for Men (SHIM) scores were identical between the two groups at 6 weeks, 3 months, and 6 months respectively. (4) Conclusion: SP EP RARP demonstrates similar performance to MP TP RARP in terms of oncologic and functional outcomes. However, SP EP RARP offers several advantages in reducing the overall hospital stay, decreasing postoperative pain and hence the overall opioid use, as well as shortening the time to catheter removal, all of which translates to reduced morbidity and facilitates the transition to outpatient surgery.
Keywords: multi-port; prostate cancer; radical prostatectomy; robotic surgery; single-port.
Conflict of interest statement
Jihad Kaouk is a Consultant for Intuitive Surgical Inc., Vascular Technology Inc. (VTI), MethodAI, and Endoquest Robotics. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Noël J., Moschovas M.C., Sandri M., Bhat S., Rogers T., Reddy S., Corder C., Patel V. Patient surgical satisfaction after da Vinci® single-port and multi-port robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy: Propensity score-matched analysis. J. Robot. Surg. 2022;16:473–481. doi: 10.1007/s11701-021-01269-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous