Treatment of Chronic Haemophilic Synovitis with PRP: Clinical and In Vitro Studies
- PMID: 39273089
- PMCID: PMC11395128
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25179140
Treatment of Chronic Haemophilic Synovitis with PRP: Clinical and In Vitro Studies
Abstract
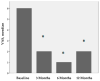
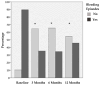
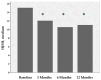
Intra-articular blood, iron and hemosiderin, hydroxyl radical cytokines, and neo-angiogenesis cause synovial inflammation, which leads to cartilage and joint damage. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) inhibits most of the mediators that produce and maintain synovitis. We compile here our work showing the clinical effectiveness of intra-articular PRP injections and their potential role in stopping articular cartilage damage due to bleeding and its possible repair. A total of 116 joints, including knees (63%), elbows (19.8%), and ankles (17.2%), were treated with intra-articular injections of PRP. Moreover, we also show here the number of extracellular DNA traps (ETs) and the PRP effect in the synovial fluid of patients at the time of treatment and six months after. Clinically, it is demonstrated that PRP is effective in reducing bleeding episodes (p < 0.001) and pain (p < 0.0001) and improving the hemophilia joint health score (HJHS) (p < 0.001) at one year of follow-up. Furthermore, our results demonstrate that PRP inhibits ET formation in vitro and reconstitutes the immune system's cellular components in the synovial fluid of patients after treatment. We conclude that PRP can be considered an effective, safe, and easy treatment for hemophilic synovitis.
Keywords: hemophilia; joint; platelet; synovitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Roosendaal G., Vianen M.E., van den Berg H.M., Lafeber F.P., Bijlsma J.W. Cartilage damage as a result of hemarthrosis in a human in vitro model. J. Rheumatol. 1997;24:1350–1354. - PubMed
-
- Hooiveld M., Roosendaal G., Vianen M., van den Berg M., Bijlsma J., Lafeber F. Blood-induced joint damage: Long term effects in vitro and in vivo. J. Rheumatol. 2003;30:339–344. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

