Spectral Characteristics, In Silico Perspectives, Density Functional Theory (DFT), and Therapeutic Potential of Green-Extracted Phycocyanin from Spirulina
- PMID: 39273119
- PMCID: PMC11394851
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25179170
Spectral Characteristics, In Silico Perspectives, Density Functional Theory (DFT), and Therapeutic Potential of Green-Extracted Phycocyanin from Spirulina
Abstract
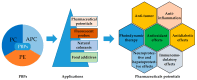
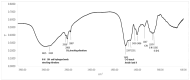
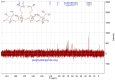
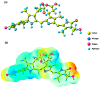
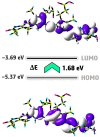
Phycocyanin (PC) is a naturally occurring green pigment in Spirulina. It was extracted by ultrasonic extraction using green technology, and its structure was studied using IR- and NMR-spectroscopy. Spectral data confirmed the PC structure. This study also involves an in silico assessment of the diverse applications of green pigment PC. Utilizing QSAR, PreADME/T, SwissADME, and Pro-Tox, this study explores the safety profile, pharmacokinetics, and potential targets of PC. QSAR analysis reveals a favorable safety profile, with the parent structure and most metabolites showing no binding to DNA or proteins. PreADME/T indicates low skin permeability, excellent intestinal absorption, and medium permeability, supporting oral administration. Distribution analysis suggests moderate plasma protein binding and cautious blood-brain barrier permeability, guiding formulation strategies. Metabolism assessments highlight interactions with key cytochrome P450 enzymes, influencing drug interactions. Target prediction analysis unveils potential targets, suggesting diverse therapeutic effects, including cardiovascular benefits, anti-inflammatory activities, neuroprotection, and immune modulation. Based on the in silico analysis, PC holds promise for various applications due to its safety, bioavailability, and potential therapeutic benefits. Experimental validation is crucial to elucidate precise molecular mechanisms, ensuring safe and effective utilization in therapeutic and dietary contexts. DFT calculations, including geometry optimization, MEP analysis, HOMO-LUMO energy surface, and quantum reactivity parameters of the PC compound, were obtained using the B3LYP/6-311G(d,p) level. This integrated approach contributes to a comprehensive understanding of PC's pharmacological profile and informs future research directions.
Keywords: DFT; FTIR spectra; NMR spectra; Spirulina; metabolism; pharmacokinetics; phycocyanin; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advances in delivery methods of Arthrospira platensis (spirulina) for enhanced therapeutic outcomes.Bioengineered. 2022 Jun;13(6):14681-14718. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2100863. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35946342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advancements in Production and Extraction Methods of Phycobiliprotein C-phycocyanin by Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis: A Mini Review.Curr Microbiol. 2024 Oct 26;81(12):428. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-03964-7. Curr Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39460769 Review.
-
Spirulina sp. LEB 18-extracted phycocyanin: Effects on liposomes' physicochemical parameters and correlation with antiradical/antioxidant properties.Chem Phys Lipids. 2021 May;236:105064. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2021.105064. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Chem Phys Lipids. 2021. PMID: 33609502
-
Green and sustainable extraction of phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis by temperature-sensitive polymer-based aqueous two-phase system and mechanism study.Bioresour Technol. 2024 Sep;407:131142. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2024.131142. Epub 2024 Jul 21. Bioresour Technol. 2024. PMID: 39043277
-
Time-temperature-resolved functional and structural changes of phycocyanin extracted from Arthrospira platensis/Spirulina.Food Chem. 2020 Jun 30;316:126374. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126374. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Food Chem. 2020. PMID: 32066073
Cited by
-
Evaluation of extra virgin olive oil compounds using computational methods: in vitro, ADMET, DFT, molecular docking and human gene network analysis study.BMC Chem. 2025 Jan 3;19(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13065-024-01369-y. BMC Chem. 2025. PMID: 39754213 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patel A., Pawar R., Mishra S., Sonawane S., Ghosh P.K. Kinetic studies on thermal denaturation of C-phycocyanin. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2004;41:254–257. - PubMed
-
- Belay A., Ota Y., Miyakawa K., Shimamatsu H. Current knowledge on potential health benefits of Spirulina. J. Appl. Phycol. 1993;5:235–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00004024. - DOI
-
- Soni R.A., Sudhakar K., Rana R.S. Spirulina–From growth to nutritional product: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017;69:157–171. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2017.09.010. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

