Thermo-Responsive Hydrogel Containing Microfluidic Chitosan Nanoparticles Loaded with Opuntia ficus-indica Extract for Periodontitis Treatment
- PMID: 39273327
- PMCID: PMC11395269
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25179374
Thermo-Responsive Hydrogel Containing Microfluidic Chitosan Nanoparticles Loaded with Opuntia ficus-indica Extract for Periodontitis Treatment
Abstract
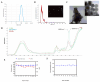
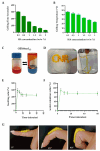
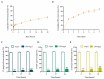
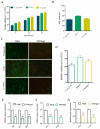
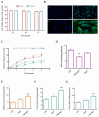
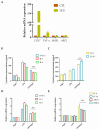
Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory disease resulting from the dysbiosis of periodontal bacteria and the host's immune response, leading to tissue degradation and sustained inflammation. Traditional treatments, such as mechanical debridement and antimicrobial agents, often fail to fully eradicate pathogenic bacteria, especially in deep periodontal pockets. Consequently, the need for novel therapeutic approaches has increased the interest in bioactive natural extracts, such as that of Opuntia ficus-indica, known for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties. This study investigates the encapsulation of Opuntia ficus-indica extract in OFI-loaded chitosan nanoparticles (OFI-NPs) via ionotropic gelation using a microfluidic system, allowing precise control over nanoparticle characteristics and enhancing protection against enzymatic degradation. To achieve localized and sustained release in periodontal pockets, a thermo-responsive hydrogel comprising hyaluronic acid and Pluronic F127 (OFI@tgels) was developed. The transition of OFI@tgels from a solution at low temperatures to a solid at body temperature enables prolonged drug release at inflammation sites. The in vitro application of the optimized formulation eradicated biofilms of S. mutans, P. aeruginosa (PAO1), and P. gingivalis over 36 h and disrupted extracellular polymeric substance formation. Additionally, OFI@tgel modulated immune responses by inhibiting M1 macrophage polarization and promoting a shift to the M2 phenotype. These findings suggest that OFI@tgel is a promising alternative treatment for periodontitis, effectively reducing biofilm formation and modulating the immune response.
Keywords: Opuntia; anti-biofilm; macrophage modulation; microfluidic particle synthesis; periodontitis; thermo-responsive hydrogel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Toledano M., Osorio M.T., Vallecillo-Rivas M., Toledano-Osorio M., Rodríguez-Archilla A., Toledano R., Osorio R. Efficacy of local antibiotic therapy in the treatment of peri-implantitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dent. 2021;113:103790. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2021.103790. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P2022RZ8WM/NextGenerationEU within the framework of National Biodiversity Future Center (NBFC);
- CN_00000033/Injectable Hydrogels for treatment of periodontal disease (HYPE). National Recovery and Resilience Plan (NRRP)
- BR22GR04/Italian Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation (MAECI), in the frame of the NANOARBO project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

