An Interplay between Transcription Factors and Recombinant Protein Synthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica at Transcriptional and Functional Levels-The Global View
- PMID: 39273402
- PMCID: PMC11395014
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25179450
An Interplay between Transcription Factors and Recombinant Protein Synthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica at Transcriptional and Functional Levels-The Global View
Abstract
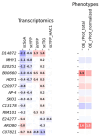
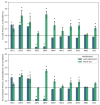
Transcriptional regulatory networks (TRNs) associated with recombinant protein (rProt) synthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica are still under-described. Yet, it is foreseen that skillful manipulation with TRNs would enable global fine-tuning of the host strain's metabolism towards a high-level-producing phenotype. Our previous studies investigated the transcriptomes of Y. lipolytica strains overproducing biochemically different rProts and the functional impact of transcription factors (TFs) overexpression (OE) on rProt synthesis capacity in this species. Hence, much knowledge has been accumulated and deposited in public repositories. In this study, we combined both biological datasets and enriched them with further experimental data to investigate an interplay between TFs and rProts synthesis in Y. lipolytica at transcriptional and functional levels. Technically, the RNAseq datasets were extracted and re-analyzed for the TFs' expression profiles. Of the 140 TFs in Y. lipolytica, 87 TF-encoding genes were significantly deregulated in at least one of the strains. The expression profiles were juxtaposed against the rProt amounts from 125 strains co-overexpressing TF and rProt. In addition, several strains bearing knock-outs (KOs) in the TF loci were analyzed to get more insight into their actual involvement in rProt synthesis. Different profiles of the TFs' transcriptional deregulation and the impact of their OE or KO on rProts synthesis were observed, and new engineering targets were pointed.
Keywords: heterologous protein; omics data; protein production; transcriptional regulation; yeast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

