Gastrodin, a Promising Natural Small Molecule for the Treatment of Central Nervous System Disorders, and Its Recent Progress in Synthesis, Pharmacology and Pharmacokinetics
- PMID: 39273485
- PMCID: PMC11394983
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25179540
Gastrodin, a Promising Natural Small Molecule for the Treatment of Central Nervous System Disorders, and Its Recent Progress in Synthesis, Pharmacology and Pharmacokinetics
Abstract
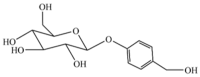
Gastrodia elata Blume is a traditional medicinal and food homology substance that has been used for thousands of years, is mainly distributed in China and other Asian countries, and has always been distinguished as a superior class of herbs. Gastrodin is the main active ingredient of G. elata Blume and has attracted increasing attention because of its extensive pharmacological activities. In addition to extraction and isolation from the original plant, gastrodin can also be obtained via chemical synthesis and biosynthesis. Gastrodin has significant pharmacological effects on the central nervous system, such as sedation and improvement of sleep. It can also improve epilepsy, neurodegenerative diseases, emotional disorders and cognitive impairment to a certain extent. Gastrodin is rapidly absorbed and widely distributed in the body and can also penetrate the blood-brain barrier. In brief, gastrodin is a promising natural small molecule with significant potential in the treatment of brain diseases. In this review, we summarised studies on the synthesis, pharmacological effects and pharmacokinetic characteristics of gastrodin, with emphasis on its effects on central nervous system disorders and the possible mechanisms, in order to find potential therapeutic applications and provide favourable information for the research and development of gastodin.
Keywords: gastrodin; pharmacokinetics; pharmacology; research progress; synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Pharmacological Effects of Gastrodin and the Progress in the Treatment of Neurological Disorders.Am J Chin Med. 2025;53(3):803-831. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X25500302. Am J Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40374368 Review.
-
The role of gastrodin in the management of CNS-related diseases: Underlying mechanisms to therapeutic perspectives.Phytother Res. 2024 Nov;38(11):5107-5133. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8314. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Phytother Res. 2024. PMID: 39148368 Review.
-
Gastrodia elata and epilepsy: Rationale and therapeutic potential.Phytomedicine. 2016 Nov 15;23(12):1511-1526. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2016.09.001. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Phytomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27765372 Review.
-
Comparative pharmacokinetics of gastrodin in rats after intragastric administration of free gastrodin, parishin and Gastrodia elata extract.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 24;176:49-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.10.007. Epub 2015 Oct 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26471288
-
Gastrodin: a comprehensive pharmacological review.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Jun;397(6):3781-3802. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02920-9. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38165423 Review.
Cited by
-
Gastrodia elata, Polygonatum sibiricum, and Poria cocos as a Functional Food Formula: Cognitive Enhancement via Modulation of Hippocampal Neuroinflammation and Neuroprotection in Sleep-Restricted Mice.Foods. 2025 Mar 22;14(7):1103. doi: 10.3390/foods14071103. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40238194 Free PMC article.
-
The protective effects of gastrodin on neurological disorders: an update and future perspectives.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 24;15:1494277. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1494277. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39776583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: Drug discovery from herbal medicines/polypeptides for neurological diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 2;16:1615452. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1615452. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40529496 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Modulation of neuroinflammation by natural plant compounds: a promising approach for ischemic stroke.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 18;16:1603417. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1603417. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40756985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastrodin attenuates rheumatoid arthritis by targeting KAT8 to inhibit the lactylation of H3K9.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 27;16:1559744. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1559744. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40213683 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taguchi H., Yosioka I., Yamasaki K., Kim I. Studies on the Constituents of Gastrodia elata BLUME. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1981;29:55–62. doi: 10.1248/cpb.29.55. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

