Dominant Chemical Interactions Governing the Folding Mechanism of Oligopeptides
- PMID: 39273531
- PMCID: PMC11395422
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25179586
Dominant Chemical Interactions Governing the Folding Mechanism of Oligopeptides
Abstract
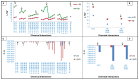
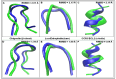
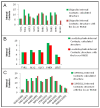
The hydrophobic effect is the main factor that drives the folding of polypeptide chains. In this study, we have examined the influence of the hydrophobic effect in the context of the main mechanical forces approach, mainly in relation to the establishment of specific interplays, such as hydrophobic and CH-π cloud interactions. By adopting three oligopeptides as model systems to assess folding features, we demonstrate herein that these finely tuned interactions dominate over electrostatic interactions, including H-bonds and electrostatic attractions/repulsions. The folding mechanism analysed here demonstrates cooperation at the single-residue level, for which we propose the terminology of "single residues cooperative folding". Overall, hydrophobic and CH-π cloud interactions produce the main output of the hydrophobic effect and govern the folding mechanism, as demonstrated in this study with small polypeptide chains, which in turn represent the main secondary structures in proteins.
Keywords: dihedral angle calculations; dominant chemical interactions; folding mechanisms; main mechanical forces.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Larocca M., Floresta G., Cilibrizzi A. Principles that Rule the Calculation of Dihedral Angles in Secondary Structures: The cases of an α-helix and a β-sheet. J. Mol. Struct. 2021;1229:129802. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.129802. - DOI
-
- Larocca M. Polypeptides folding: Rules for the calculation of the backbone dihedral angles ϕ starting from the amino acid sequence. ChemRxiv. 2020:Preprint. doi: 10.26434/chemrxiv.12000132.v2. - DOI
-
- Larocca M., Floresta G., Verderese D., Cilibrizzi A. ‘Main Mechanical Forces-Chemical Interactions’ Interplay as a Tool to Elucidate Folding Mechanisms. Pept. Sci. :2024. doi: 10.1002/pep2.24365. in press. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

