Investigating the Anti-Inflammatory, Analgesic, and Chondroprotective Effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.) Makino in Osteoarthritis: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study
- PMID: 39273553
- PMCID: PMC11395165
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25179594
Investigating the Anti-Inflammatory, Analgesic, and Chondroprotective Effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.) Makino in Osteoarthritis: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study
Abstract
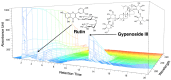
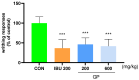
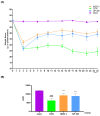
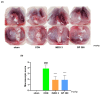
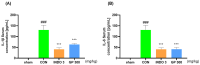
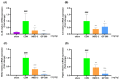
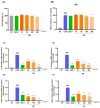
Osteoarthritis (OA) is an age-related disease characterized by inflammation, pain, articular cartilage damage, synovitis, and irreversible disability. Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.) Makino (GP), a herbal medicine traditionally used in East Asia for its anti-inflammatory properties, was investigated for its potential to modulate OA pathology and symptoms. This study evaluated GP's efficacy in inhibiting pain, functional decline, and cartilage destruction in monosodium iodoacetate-induced OA and acetic acid-induced writhing models. Additionally, the effects of GP on OA-related inflammatory targets were assessed via mRNA and protein expression in rat knee cartilage and lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 cells. The GP group demonstrated significant pain relief, functional improvement, and cartilage protection. Notably, GP inhibited key inflammatory mediators, including interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-3 and MMP-13, cyclooxygenase-2, and prostaglandin E receptor 2, surpassing the effects of active controls. These findings suggest that GP is a promising candidate for disease-modifying OA drugs and warrants further comprehensive studies.
Keywords: Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.) Makino; analgesic; anti-inflammatory; chondroprotective; herbal medicine; osteoarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Hee-Geun Jo was employed by the company Naturalis Inc. Author Eunhye Baek was employed by the company RexSoft Inc. All the authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. In addition, there is no significant financial support affecting the outcomes of this study.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

