Characteristics of a Novel Zearalenone Lactone Hydrolase ZHRnZ and Its Thermostability Modification
- PMID: 39273612
- PMCID: PMC11395237
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25179665
Characteristics of a Novel Zearalenone Lactone Hydrolase ZHRnZ and Its Thermostability Modification
Abstract
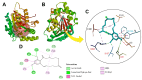
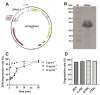
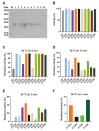
Zearalenone (ZEN) is a toxic secondary metabolite produced by the Fusarium fungi, which widely contaminates grains, food, and feed, causing health hazards for humans and animals. Therefore, it is essential to find effective ZEN detoxification methods. Enzymatic degradation of ZEN is believed to be an eco-friendly detoxification strategy, specifically thermostable ZEN degradation enzymes are needed in the food and feed industry. In this study, a novel ZEN lactone hydrolase ZHRnZ from Rosellinia necatrix was discovered using bioinformatic and molecular docking technology. The recombinant ZHRnZ showed the best activity at pH 9.0 and 45 °C with more than 90% degradation for ZEN, α-zearalenol (α-ZOL), β-zearalenol (β-ZOL) and α-zearalanol (α-ZAL) after incubation for 15 min. We obtained 10 mutants with improved thermostability by single point mutation technology. Among them, mutants E122Q and E122R showed the best performance, which retained more than 30% of their initial activity at 50 °C for 2 min, and approximately 10% of their initial activity at 60 °C for 1 min. The enzymatic kinetic study showed that the catalytic efficiency of E122R was 1.3 times higher than that of the wild-type (WT). Comprehensive consideration suggests that mutant E122R is a promising hydrolase to detoxify ZEN in food and feed.
Keywords: lactone hydrolase; mutation; thermostability; zearalenone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
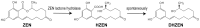



References
-
- Fruhauf S., Novak B., Nagl V., Hackl M., Hartinger D., Rainer V., Labudová S., Adam G., Aleschko M., Moll W.-D., et al. Biotransformation of the Mycotoxin Zearalenone to Its Metabolites Hydrolyzed Zearalenone (HZEN) and Decarboxylated Hydrolyzed Zearalenone (DHZEN) Diminishes Its Estrogenicity In Vitro and In Vivo. Toxins. 2019;11:481. doi: 10.3390/toxins11080481. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

