Applying UHPLC-HRAM MS/MS Method to Assess Host Cell Protein Clearance during the Purification Process Development of Therapeutic mAbs
- PMID: 39273634
- PMCID: PMC11396427
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25179687
Applying UHPLC-HRAM MS/MS Method to Assess Host Cell Protein Clearance during the Purification Process Development of Therapeutic mAbs
Abstract
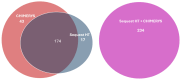
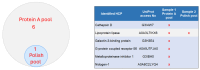
Host cell proteins (HCPs) are one of the process-related impurities that need to be well characterized and controlled throughout biomanufacturing processes to assure the quality, safety, and efficacy of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and other protein-based biopharmaceuticals. Although ELISA remains the gold standard method for quantification of total HCPs, it lacks the specificity and coverage to identify and quantify individual HCPs. As a complementary method to ELISA, the LC-MS/MS method has emerged as a powerful tool to identify and profile individual HCPs during the downstream purification process. In this study, we developed a sensitive, robust, and reproducible analytical flow ultra-high-pressure LC (UHPLC)-high-resolution accurate mass (HRAM) data-dependent MS/MS method for HCP identification and monitoring using an Orbitrap Ascend BioPharma Tribrid mass spectrometer. As a case study, the developed method was applied to an in-house trastuzumab product to assess HCP clearance efficiency of the newly introduced POROS™ Caprylate Mixed-Mode Cation Exchange Chromatography resin (POROS Caprylate mixed-mode resin) by monitoring individual HCP changes between the trastuzumab sample collected from the Protein A pool (purified by Protein A chromatography) and polish pool (purified by Protein A first and then further purified by POROS Caprylate mixed-mode resin). The new method successfully identified the total number of individual HCPs in both samples and quantified the abundance changes in the remaining HCPs in the polish purification sample.
Keywords: HPLC MS/MS method; host cell proteins; process related HCP profiling.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors were employed by the company Thermo Fisher Scientific. All authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Molden R., Hu M., Yen E.S., Saggese D., Reilly J., Mattila J., Qiu H., Chen G., Bak H., Li N. Host cell protein profiling of commercial therapeutic protein drugs as a benchmark for monoclonal antibody-based therapeutic protein development. mAbs. 2021;13:1955811. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2021.1955811. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

