A Hypoxia-Decidual Macrophage Regulatory Axis in Normal Pregnancy and Spontaneous Miscarriage
- PMID: 39273657
- PMCID: PMC11395248
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25179710
A Hypoxia-Decidual Macrophage Regulatory Axis in Normal Pregnancy and Spontaneous Miscarriage
Abstract
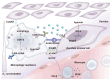
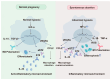
The significance of hypoxia at the maternal-fetal interface is proven to be self-explanatory in the context of pregnancy. During the first trimester, low oxygen conditions play a crucial role in processes such as angiogenesis, trophoblast invasion and differentiation, and immune regulation. Recently, there has been increasing research on decidual macrophages, which contribute to the maintenance of immune tolerance, placental and fetal vascular development, and spiral artery remodeling, to investigate the effects of hypoxia on their biological behaviors. On these grounds, this review describes the dynamic changes in oxygen levels at the maternal-fetal interface throughout gestation, summarizing current knowledge on how the hypoxic environment sustains a successful pregnancy by regulating retention, differentiation and efferocytosis of decidual macrophages. Additionally, we explore the relationship between spontaneous miscarriages and an abnormal hypoxia-macrophage axis, shedding light on the underlying mechanisms. However, further studies are essential to elucidate these pathways in greater detail and to develop targeted interventions that could improve pregnancy outcomes.
Keywords: abortion; decidual macrophage; hypoxia; polarization; retention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

