Interaction of Micro- and Nanoplastics with Enzymes: The Case of Carbonic Anhydrase
- PMID: 39273668
- PMCID: PMC11396312
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25179716
Interaction of Micro- and Nanoplastics with Enzymes: The Case of Carbonic Anhydrase
Abstract
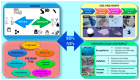
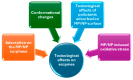
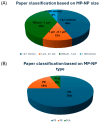
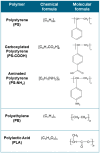
Microplastics (MPs) and nanoplastics (NPs) have emerged as significant environmental pollutants with potential detrimental effects on ecosystems and human health. Several studies indicate their interaction with enzymes; this topic represents a multifaceted research field encompassing several areas of interest from the toxicological and ecotoxicological impact of MPs and NPs on humans and wildlife to the biodegradation of plastics by microbial enzymes. This review aims to provide a critical analysis of the state-of-the-art knowledge of the interaction of MPs and NPs on the enzyme carbonic anhydrase (CA), providing recent insights, analyzing the knowledge gaps in the field, and drawing future perspectives of the research and its application. CA is a widespread and crucial enzyme in various organisms; it is critical for various physiological processes in animals, plants, and bacteria. It catalyzes the reversible hydration of CO2, which is essential for respiration, acid-base balance, pH homeostasis, ion transport, calcification, and photosynthesis. Studies demonstrate that MPs and NPs can inhibit CA activity with mechanisms including adsorption to the enzyme surface and subsequent conformational changes. In vitro and in silico studies highlight the role of electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions in these processes. In vivo studies present mixed results, which are influenced by factors like particle type, size, concentration, and organism type. Moreover, the potentiality of the esterase activity of CA for plastic degradation is discussed. The complexity of the interaction between CA and MPs/NPs underscores the need for further research to fully understand the ecological and health impacts of MPs and NPs on CA activity and expression and glimpses of the potentiality and perspectives in this field.
Keywords: biomarker; carbonic anhydrase; ecotoxicological effects; emergent pollutant; enzymes; esterase activity; microplastics; nanoplastics; plastic degradation; toxicological effects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mojiri A., Vishkaei M.N., Zhou J.L., Trzcinski A.P., Lou Z., Kasmuri N., Rezania S., Gholami A., Vakili M., Kazeroon R.A. Impact of polystyrene microplastics on the growth and photosynthetic efficiency of diatom Chaetoceros neogracile. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024;194:106343. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2024.106343. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mutuku J., Yanotti M., Tocock M., Hatton MacDonald D. The Abundance of Microplastics in the World’s Oceans: A Systematic Review. Oceans. 2024;5:398–428. doi: 10.3390/oceans5030024. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

