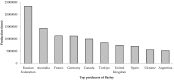
Unraveling the Hidden Potential of Barley (Hordeum vulgare): An Important Review
- PMID: 39273905
- PMCID: PMC11397514
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13172421
Unraveling the Hidden Potential of Barley (Hordeum vulgare): An Important Review
Abstract
Barley (Hordeum vulgare) is a winter crop well known for its small-seeded grains and self-pollinating characteristics. The flour derived from barley grains plays a crucial role in numerous processed food items, contributing to their taste and nutritional value. Barley consists of complex carbohydrates (80%), proteins (11.5-14.2%), lipids (4.7-6.8%), β-glucans (3.7-7.7%), and ash (1.8-2.4%). Beyond its other nutrients, barley boasts a good reservoir of phenolic compounds (1.2-2.9 mg/g GAE). This abundance of beneficial compounds positions barley as an attractive industrial substrate. In this review, the nutritional composition and bioactive profile of barley are discussed in a systemic manner, emphasizing its potential in the development of innovative barley-based products that promote health and well-being. By incorporating barley into various food formulations, industries can not only boost nutritional content but also offer consumers a wide range of health benefits. In conclusion, barley's diverse applications in food and health highlight its essential role in promoting healthier living.
Keywords: barley; bioactive profile; food; nutritional composition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Salar R.K., Purewal S.S., Sandhu K.S. Relationships between DNA damage protection activity, total phenolic content, condensed tannin content and antioxidant potential among Indian barley cultivars. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017;11:201–206. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2017.07.006. - DOI
-
- Boukid F. Comprehensive review of barley dietary fibers with Emphasis on arabinoxylans. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre. 2024;31:100410. doi: 10.1016/j.bcdf.2024.100410. - DOI
-
- Raj R., Shams R., Pandey V.K., Dash K.K., Singh P., Bashir O. Barley phytochemicals and health promoting benefits: A comprehensive review. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023;14:100677. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2023.100677. - DOI
-
- Lazaridou A., Kotsiou K., Biliaderis C.G. Nutritional and technological aspects of barley β-glucan enriched biscuits containing isomaltulose as sucrose replacer. Food Hydrocoll. Health. 2022;2:100060. doi: 10.1016/j.fhfh.2022.100060. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous